AUTOGEN | 上手与源码分析
AUTOGEN 是一个开源平台,主要用于创建和管理自动化对话代理(agents)。这些代理可以完成多种任务,比如回答问题、执行函数,甚至与其他代理进行交互。
本文旨在介绍 Autogen 中的关键组件 Conversation Agent,并对其中的 Multi-Agent 功能实现做简单的源码分析。
参考官网文档,参考代码 Autogen 源码5a5c0f2 。
1. Autogen Agent 实现
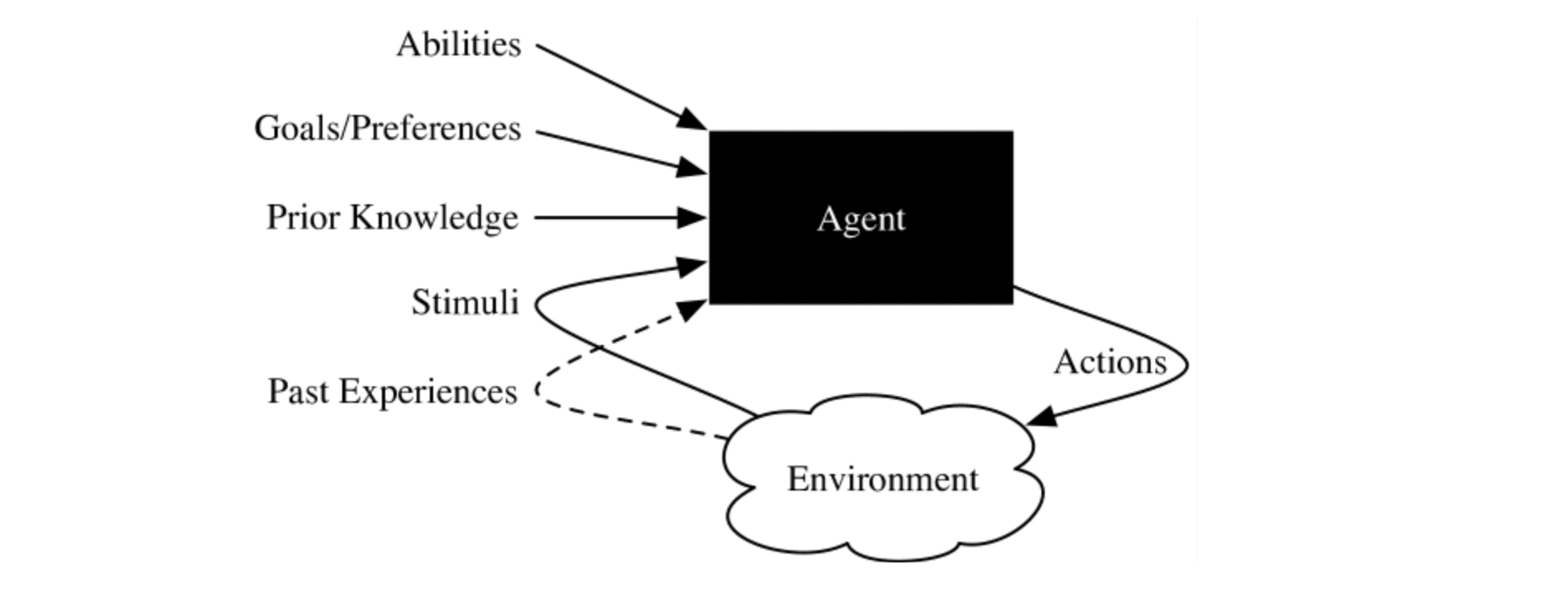
Autogen 中 agent 的设计思路大致为:
Abilities & Prior Knowledge
- 逻辑思考能力:
和大多数智能体设计一样,Autogen 使用了语言模型(LLM)作为逻辑单元。它通过调用 OpenAI 的 Python SDK 来访问 LLM 服务。因此,任何部署了 OpenAI Compatible API 的 LLM 都可以无缝对接到 Autogen。
- 工具选择的能力
Autogen 利用了 openai 提供的 Tool(Functions)功能 来调用函数,而不是使用自定义提示来引导逻辑模型选择工具。调用 Openai 服务时,在请求体的 tools 中提供候选函数的信息,Openai API 就会从中选出最可能实现用户诉求的函数。
查看示例 openai 调用 tools 请求
示例请求
curl https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-4-turbo",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What'\''s the weather like in Boston today?"
}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
}
],
"tool_choice": "auto"
}'
示例回复
{
"id": "chatcmpl-abc123",
"object": "chat.completion",
"created": 1699896916,
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo-0125",
"choices": [
{
"index": 0,
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_abc123",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"arguments": "{\n\"location\": \"Boston, MA\"\n}"
}
}
]
},
"logprobs": null,
"finish_reason": "tool_calls"
}
],
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 82,
"completion_tokens": 17,
"total_tokens": 99
}
}
- 通信功能
每个 agent 都可以使用自带的 send 和 receive 方法和其他 agent 进行通信。
Action & Stimuli
智能体在选择了合适的工具后,可以执行该工具并接收工具返回的结果。
Goals/Preference
Autogen 通过为不同的智能体提供不同的系统提示词来实现个性化设置。
Past Experience
每个智能体都会维护自己的历史记录,以 List[Message] 的形式保存,其中 Message 包括了历史对话信息和执行函数的结果等
2. Autogen 部分细节
2.1 Conversable Agent
Conversable Agent 是 Autogen 中的基本智能体类型,其他如 AssistantAgent 或 UserProxyAgent 都是基于此类实现的。
2.1.1 为 Conversable Agent 配置 LLM
初始化 Conversable Agent 时提供的 config_list,都会被用来初始化 openai OpenAI 对象。如通过以下方法创建 conversable Agent 实例后
from autogen import ConversableAgent
config_list = [
{
"api_type": "azure",
"model": AZURE_OPENAI_CHAT_DEPLOYMENT_NAME,
"api_key": AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY,
"http_client": xxxxx, # 确保传入的是可以进行 deepcopy 的对象
"base_url": AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT,
}
]
agent = ConversableAgent("chatbot",llm_config={"config_list": config_list})
此时,Conversable Agent 会使用类似以下的方式创建 OpenAI 实例:
client = AzureOpenAI(**config_list)
以上为伪代码,具体实现参考源码。
2.1.2 Generate Reply
generate_reply 是 Conversable Agent 的核心功能之一。此函数会根据接收到的消息和配置,通过一系列注册的处理函数和回复生成函数,来产生一个回复。例如:
reply = agent.generate_reply(messages=[{"content": "你好", "role": "user"}])
print(reply) # 你好,有什么可以帮助你的?
此过程包括消息的预处理、历史消息的整理和回复的生成等步骤,允许通过定制化的钩子(hook)来处理特定的逻辑。为了考虑到 agent 调用工具,对话,参考历史经验等功能,generate_reply 的大致运行思路如下:
- 步骤一:处理最后接收的消息(process_last_received_message)
此功能通过注册的钩子(hook)使用并可能修改最后一条消息的文本:
messages = self.process_last_received_message(messages)
我们只需要再 self.hook_lists['process_last_received_message'] 中添加对应的函数,就能自定义处理消息的方法:
# process_last_received_message 伪代码
def process_last_received_message(messages):
for hook in self.hook_lists['process_last_received_message']:
messages[-1]["content"] = hook(messages[-1]["content"])
return messages
具体参考 process_last_received_message 。
- 步骤二:处理回复前的所有消息(process_all_messages_before_reply)
这一步骤与处理最后接收的消息相似,使用相同的逻辑。我们只需要再 self.hook_lists['process_all_messages_before_reply'] 中添加对应的函数,就能自定义处理消息的方法。
因为 LLM 上下文长度有限,因此通常这步可以用来对历史信息进行整理,筛选等等。
具体参考 process_all_messages_before_reply
- 步骤三:生成回复(generate_reply)
Autogen 把多种不同功能的 agent 都整合到了 Conversable Agent 当中,agent 生成回复时的逻辑大致如下:
# 伪代码
for reply_func_tuple in self._reply_func_list:
final, reply = reply_func(messages=messages, sender=sender, config=reply_func_tuple["config"])
if final:
return reply
默认情况下,self._reply_func_list 中包含以下几个函数:
self._reply_func_list = [ConversableAgent.check_termination_and_human_reply,
ConversableAgent.generate_function_call_reply,
ConversableAgent.generate_tool_calls_reply,
ConversableAgent.generate_oai_reply]
通过 messages 来判断现在时候需要终止 agent 对话,或者需要认为接入。
例如:当最后一个消息中包含了特定的终止字符;或对话轮数达到了上限等等。终止字符和对话上限都可以自定义。
- generate_function_call_reply
可以忽略这个函数,因为他被 generate_tool_calls_reply 取代了,基本上用不到
该函数给工具型的 agent 执行,llm 型的 agent 默认不触发。
例如参考 autogen 官方的 Tool 使用示例 配置后:
from typing import Annotated, Literal
Operator = Literal["+", "-", "*", "/"]
def calculator(a: int, b: int, operator: Annotated[Operator, "operator"]) -> int:
if operator == "+":
return a + b
elif operator == "-":
return a - b
elif operator == "*":
return a * b
elif operator == "/":
return int(a / b)
else:
raise ValueError("Invalid operator")
user_proxy = ConversableAgent(
name="User",
llm_config=False,
human_input_mode="NEVER"
)
user_proxy.register_for_execution(name="calculator")(calculator)
reply = user_proxy.generate_reply(messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "", "tool_calls": [
{
"id": "123",
"function": {
"name": "calculator",
"arguments": '{"a": 232, "b": 40, "operator": "-"}'
}
}
]}])
"""
reply == {'role': 'tool',
'tool_responses': [{'tool_call_id': '123', 'role': 'tool', 'content': '192'}],
'content': '192'}
"""
user_proxy 调用 generate_reply 时就会执行generate_tool_calls_reply 。大致思路就是把输入的 tool_calls 的参数,传递给对应的函数执行,然后返回函数执行的结果。
调用 LLM 服务,根据当前的 messages 来生成回复。该函数分为 2 种情况,关联了函数,和不关联函数:
不关联函数:
默认情况下 Conversable Agent 是不关联函数的。如:
from autogen import ConversableAgent
agent = ConversableAgent("chatbot",llm_config={"config_list": config_list})
# 没有注册 tool 时候,使用 generate_reply
reply = agent.generate_reply(messages=[{"content": "What is 1+1.", "role": "user"}])
没有注册 tool 时候发给 openai 的请求
"""
发给 openai 的 payload
{'messages': [{'content': "You are a helpful AI assistant. You can help with simple calculations. Return 'TERMINATE' when the task is done.",
'role': 'system'}, {'content': 'What is 1+1.', 'role': 'user'}], 'model': 'gpt-4-128k-0125'}
"""
不关联函数时,就像和 GPT 对话一样回复正常内容。
关联函数:
给 agent 关联函数之后,在生成回复时,会考虑是否需要使用函数工具,如参考官方文档,为 agent 注册函数:
assistant.register_for_llm(name="calculator", description="A simple calculator")(calculator)
然后调用 generate_reply:
# 有注册 tool 时候,使用 generate_reply
reply_2 = assistant.generate_reply(messages=[{"content": "What is 1+1.", "role": "user"}])
有注册 tool 时候发给 openai 的请求
{
"messages": [
{
"content": "You are a helpful AI assistant. You can help with simple calculations. Return "TERMINATE" when the task is done.",
"role": "system"
},
{
"content": "What is 1+1.",
"role": "user"
}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"description": "A simple calculator",
"name": "calculator",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"a": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "a"
},
"b": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "b"
},
"operator": {
"enum": [
"+",
"-",
"*",
"/"
],
"type": "string",
"description": "operator"
}
},
"required": [
"a",
"b",
"operator"
]
}
}
}
],
"model": "gpt-4-128k-0125"
}
回复结果格式为:
{'content': None,
'role': 'assistant',
'function_call': None,
'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_dBSB0eUcGXqPjmSvLEpbf8t6',
'function': {'arguments': '{"a":1,"b":1,"operator":"+"}',
'name': 'calculator'},
'type': 'function'}]}
Generate Reply 总结
整体伪代码如下:
def generate_reply(messages: List[], sender: [Agent] ):
# 处理最后接收的消息,可以插入自定义 hook
for hook in self.hook_lists['process_last_received_message']:
messages[-1]["content"] = hook(messages[-1]["content"])
# 处理所有历史消息,可以插入自定义 hook
for hook in self.hook_lists['process_all_messages_before_reply']:
messages = hook(messages)
self._reply_func_list = [
# self._reply_func_list 可以插入自定义函数
your_customized_function,
# 如果达到了终止条件,则后续函数都不会执行
ConversableAgent.check_termination_and_human_reply,
# 当 llm_config=False, 并且注册了函数执行
ConversableAgent.generate_tool_calls_reply,
# 当 llm_config!=False 执行
ConversableAgent.generate_oai_reply
]
for reply_func_tuple in self._reply_func_list:
final, reply = reply_func(messages=messages, sender=sender, config=reply_func_tuple["config"])
if final:
return reply
2.1.3 代码执行器(Code Executor)
通过自定义的本地命令行代码执行器,代理可以安全地执行 GPT 生成的代码。AutoGPT 自带 docker, jupter 和 local 三种代码执行器。
import tempfile
from autogen import ConversableAgent
from autogen.coding import LocalCommandLineCodeExecutor
temp_dir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory()
executor = LocalCommandLineCodeExecutor(timeout=10, work_dir=temp_dir.name)
code_executor_agent = ConversableAgent("code_executor_agent", code_execution_config={"executor": executor})
message_with_code_block = """This is a message with code block.
The code block is below:
```
print(1+asdf)
```
```
print("second")
```
This is the end of the message.
"""
# Generate a reply for the given code.
reply = code_executor_agent.generate_reply(messages=[{"role": "user", "content": message_with_code_block}])
print(reply)
代码执行器的思路为
- 首先在
self._reply_func_list插入 _generate_code_execution_reply_using_executor 函数。 - 以上函数会先使用 markdown 解析器来从输入的 message 种提取代码。
- 而后使用执行器来执行抽取出来的代码。
如果需要自定义代码解析和执行方式的话,只需要参考 LocalCommandLineCodeExecutor 集成 CodeExecutor 并重写 code_extractor 和 execute_code_blocks 。
2.1.4 Init Chat
通过上文可以看到 Autogen 对 ConversableAgent 的包装,并不符合 Agent 的定义:
- 当 ConversableAgent 设置了
lm_config=False,并注册了函数后,改 Agent 相当于一个指挥执行函数的工具。 - 如果需要设计一个会使用函数的 Agent 的话,那么需要用 2 个 ConversableAgent 来实现,具体参考官网文档。
所有 ConversableAgent 间的对话都通过 initiate_chat 函数启动,通过 send 和 receive 函数进行消息传递,确保信息正确接收。而这种设置,是的开发者可以使用多个 ConversableAgent 来灵活搭配,组合出他们想要得 Agent 系统。如:
等其他系统。
initiate_chat 使用案例:
# 实现一个可以使用外部 python 函数的助手
chat_result = user_proxy.initiate_chat(assistant, message="What is (44232 + 13312 / (232 - 32)) * 5?")
initiate_chat 实现逻辑:
# 伪代码
def initiate_chat(recipient, message, clear_history, *args):
# 可以配置 clear_history 来清空历史记录
self._prepare_chat(recipient, clear_history)
# 可设置 agent 最多对话回合数
for _ in range(max_turns):
if _ == 0:
# 对 message 进行了一些简单的格式预处理
msg2send = self.generate_init_message(message, **kwargs)
else:
# 使用 generate_reply ,根据 message 生成回复
msg2send = self.generate_reply(messages=self.chat_messages[recipient], sender=recipient)
if msg2send is None:
break
# 发送消息给下一个 Agent
self.send(msg2send, recipient, request_reply=True, silent=silent)
summary = self._summarize_chat(...)
chat_result = ChatResult(...)
return chat_result
以上 init_chat 的核心在于 send 函数:
# 伪代码
def send(self, message: Union[Dict, str], recipient: Agent,
request_reply: Optional[bool] = None):
return recipient.receive(message, self, request_reply, silent)
def receive(self, message: Union[Dict, str], sender: Agent, request_reply: Optional[bool] = None,):
reply = self.generate_reply(messages=self.chat_messages[sender], sender=sender)
if reply is not None:
self.send(reply, sender, silent=silent)
因此,autogen 设计的 send 和 receive 函数形成了一个闭环,只要 generate_reply 不因为 ConversableAgent.check_termination_and_human_reply 被终止,那么这两个 Agent 就会一直对话下去。
当然,initiate chat 中还有很多有意思的设计,具体请参考 inititate_chat 源码。
2.2 Multi-Agent
通过以上 initiate_chat 我们大致清楚了 2 个 Agent 是怎么对话的:
- 通过
send和receive函数实现闭环对话。
那如果我们想要让 2 个以上的 agent 进行对话,可以使用 Autogen 包装好的 GroupChat。
GroupChat 的实现逻辑大致为:
- 建立一个 GroupManager 来扮演邮差的角色。
- 所有 Group 里的 Agent 不直接对话,而是通过 GroupManager 实现对话的传递。
这种 GroupChat 的设计方式允许我们设计自由讨论的 Multi-agent,同时也可以实现固定 flow 的 Multi-Agent 工作流。
具体可以参考:link
3. 其他
开源社区贡献autogen.agentchat.contrib 这里可以找到许多关于自动化对话系统的贡献。
Agent 优化器
官方 notebook 中有关于 Agent 优化器的讨论。link
自定义输出
Autogen 默认将 Agent 对话信息输出在终端中。如果想在前端展示,可以使用官方提供的 WebSocketIO,将对话信息以 stream 的形式输出到 UI 界面。
4. 总结
Autogen 作为 Agent 搭建工具,提供了一些基础功能。虽然其设计将执行工具与 LLM Agent 合并在一起,但这种设计在某些情况下并不优雅,可以考虑将函数工具与 LLM Agent 分开设计。
此外 Autogen 中, 2 个 Agent 之间的对话,是通过递归函数实现的;Multi-Agent 对话是通过邮差传话的形式实现的。