Function Call 整理
在本文中,我们梳理了开源模型 Function Calling 能力的相关信息,包括采用的 chat template,function call 训练方案等。涉及模型 LlaMa 3.1, Mistral Large 2,glm-4-9b-chat,Qwen 2。
Llama 3.1
推荐官方指南:https://llama.meta.com/docs/model-cards-and-prompt-formats/llama3_1/
对话协议(Chat Protocal)
Llama 3.1 中采用了以下 special tokens 来辅助多轮对话和工具的调用。。
<|begin_of_text|>: 指定 prompt 的开始<|end_of_text|>: 模型将停止生成更多的 tokens。此 token 仅由基础模型生成。<|start_header_id|>和<|end_header_id|>: 这些 tokens 封闭特定消息的角色。可能的角色包括:[system, user, assistant, and ipython]<|eom_id|>: end of message。表示消息结束,提示模型接下来可能需要调用工具。这用于模型与任何可用工具之间的多步骤交互。当在系统提示中使用Environment: ipython指令时,或者如果模型调用内置工具时,会发出此 token。<|eot_id|>: End of turn。表示模型已经确定它已完成与用户消息的互动,有两种情况会使用:- 在模型与用户之间的直接互动结束时
- 在模型与任何可用工具之间的多次互动结束时
<|python_tag|>: 是模型响应中用来表示工具调用的特殊标签。
在对话过程中,llama 3.1 支持了 4 中角色:
[system, assistant, user, ipython] 其中 ipython 的角色与 gpt 中的 tool 类似,用来标记调用 tool 后生成的结果。
Tool Call Template 样式
根据 Llama 的这个技术报告 来看,llama 3 工具调用能力,是在 post training 的时候加上去的。大致的使用 tool 流程和 GPT 的 tool call 差不多,如下: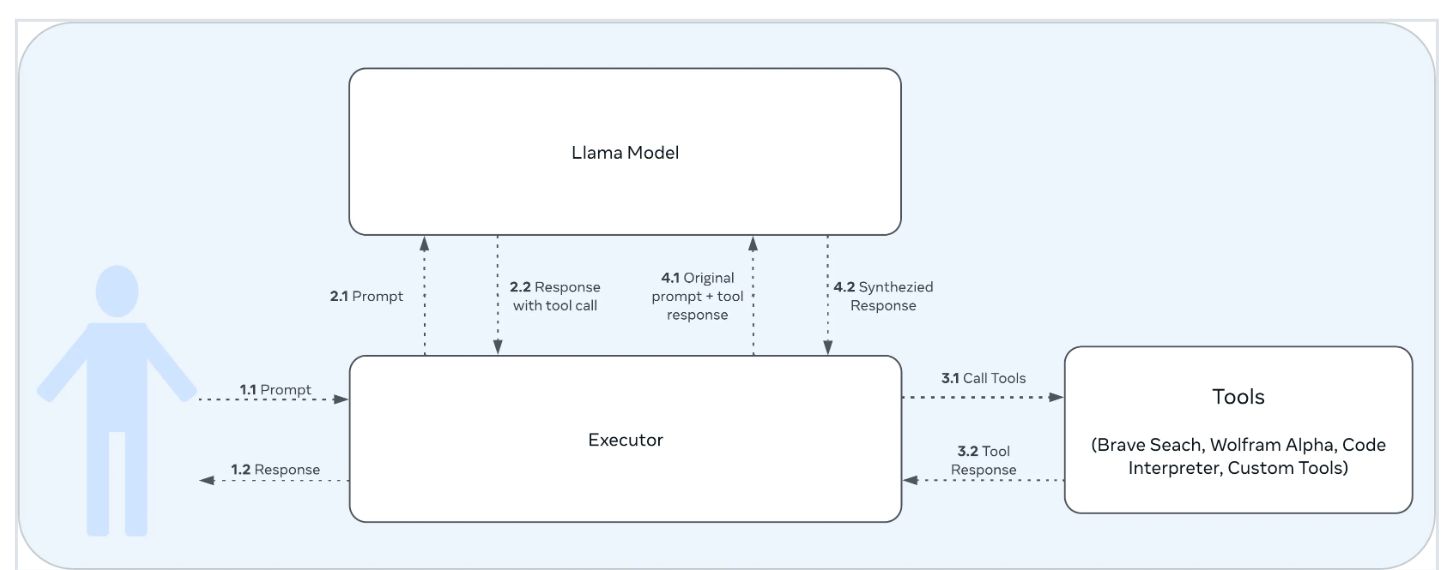
样式 1:Json based tool calling
以下用一个例子展示 llama 3.1 tool call 时候的格式,假设用户与 agent 有了以下对话:
tool_call = {"name": "get_current_temperature", "arguments": {"location": "Paris, France"}}
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a bot that responds to weather queries."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Hey, what's the temperature in Paris right now?"},
{"role": "assistant", "tool_calls": [{"type": "function", "function": tool_call}]},
{"role": "tool", "name": "get_current_temperature", "content": "22.0"}
]
那么,此时的 prompt 为:
<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>
Environment: ipython
Cutting Knowledge Date: December 2023
Today Date: 26 Jul 2024
You have access to the following functions. To call a function, please respond with JSON for a function call.Respond in the format {"name": function name, "parameters": dictionary of argument name and its value}.Do not use variables.
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"description": "Get the current temperature at a location.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The location to get the temperature for, in the format \"City, Country\""
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
},
"return": {
"type": "number",
"description": "The current temperature at the specified location in the specified units, as a float."
}
}
}
You are a bot that responds to weather queries.<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>
Hey, what's the temperature in Paris right now?<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
{"name": "get_current_temperature", "parameters": {"location": "Paris, France"}}<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>ipython<|end_header_id|>
"22.0"<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
关注点:
- 为了方便阅读,以上 prompt 中添加了一些换行符。
- llama 3.1 70B instruct 提供的模板中,可以选择将 function 信息放在用户的输入中,或者放在 system prompt 中。
- 工具调用结果通过
<|start_header_id|>ipython<|end_header_id|>标记。 - 在 llama 3.1 的官方文档中还记录了一种 User-defined Custom tool calling 的方法,但是没有在 llama3.1 70B instruct 的 jinja chat template 中找到对应的功能,可能官方还没更新 jinja template?
具体生成以上 prompt 的代码
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
model_path = "/home/kevin/models/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct"
# First, define a tool
def get_current_temperature(location: str) -> float:
"""
Get the current temperature at a location.
Args:
location: The location to get the temperature for, in the format "City, Country"
Returns:
The current temperature at the specified location in the specified units, as a float.
"""
return 22. # A real function should probably actually get the temperature!
tool_call = {"name": "get_current_temperature", "arguments": {"location": "Paris, France"}}
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a bot that responds to weather queries."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Hey, what's the temperature in Paris right now?"},
{"role": "assistant", "tool_calls": [{"type": "function", "function": tool_call}]},
{"role": "tool", "name": "get_current_temperature", "content": "22.0"}
]
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True)
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages,
tools=[get_current_temperature],
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=False,
tools_in_user_message=False)
with open("input.txt", 'w') as fp:
fp.write(inputs)
更具体的多轮对话 prompt 可以参考 llama 3.1-70b-instruct 的 jinja chat template。
样式 2:Built in Python based tool calling
官方自带支持 brave_search, wolfram_alpha, 和 code interpreter 三种工具,使用这三种工具时,tokenizer 的处理方式与 json based tool calling 不太一样。具体是要在 system prompt 中加上
Environment: ipython
Tools: brave_search, wolfram_alpha
同时模型要调用工具时,会生成 <|python_tag|>wolfram_alpha.call(query="solve x^3 - 4x^2 + 6x - 24 = 0")<|eom_id|> 类似的样式,而非原先的 json 格式:
<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>
Environment: ipython
Tools: brave_search, wolfram_alpha
Cutting Knowledge Date: December 2023
Today Date: 23 Jul 2024
You are a helpful assistant.<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>
Can you help me solve this equation: x^3 - 4x^2 + 6x - 24 = 0<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
<|python_tag|>wolfram_alpha.call(query="solve x^3 - 4x^2 + 6x - 24 = 0")<|eom_id|>
<|start_header_id|>ipython<|end_header_id|>
{"queryresult": {"success": true, "inputstring": "solve x^3 - 4x^2 + 6x - 24 = 0", "pods": [{"title": "Input interpretation", "subpods": [{"title": "", "plaintext": "solve x^3 - 4 x^2 + 6 x - 24 = 0"}]}, {"title": "Results", "primary": true, "subpods": [{"title": "", "plaintext": "x = 4"}, {"title": "", "plaintext": "x = \u00b1 (i sqrt(6))"}]}, ... ]}}<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
工具调用相关的训练
The Llama 3 Herd of Models 中提到工具调用是在 post training 部分加上去的,包括了多组的 SFT + DPO 训练。
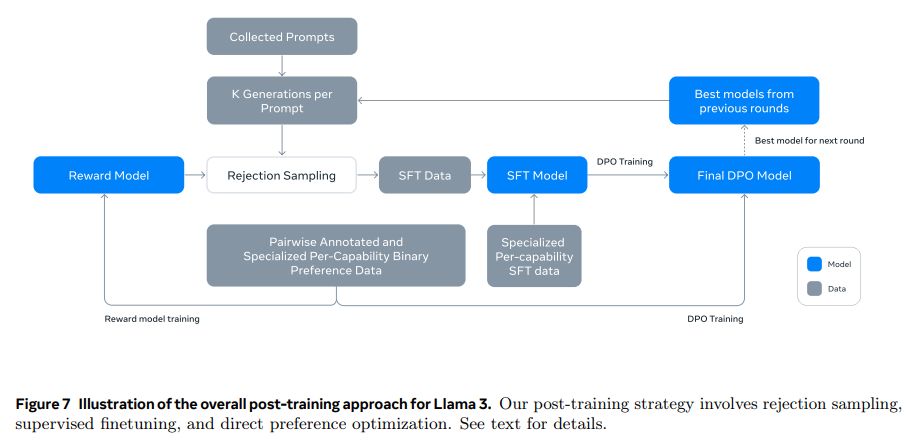
SFT
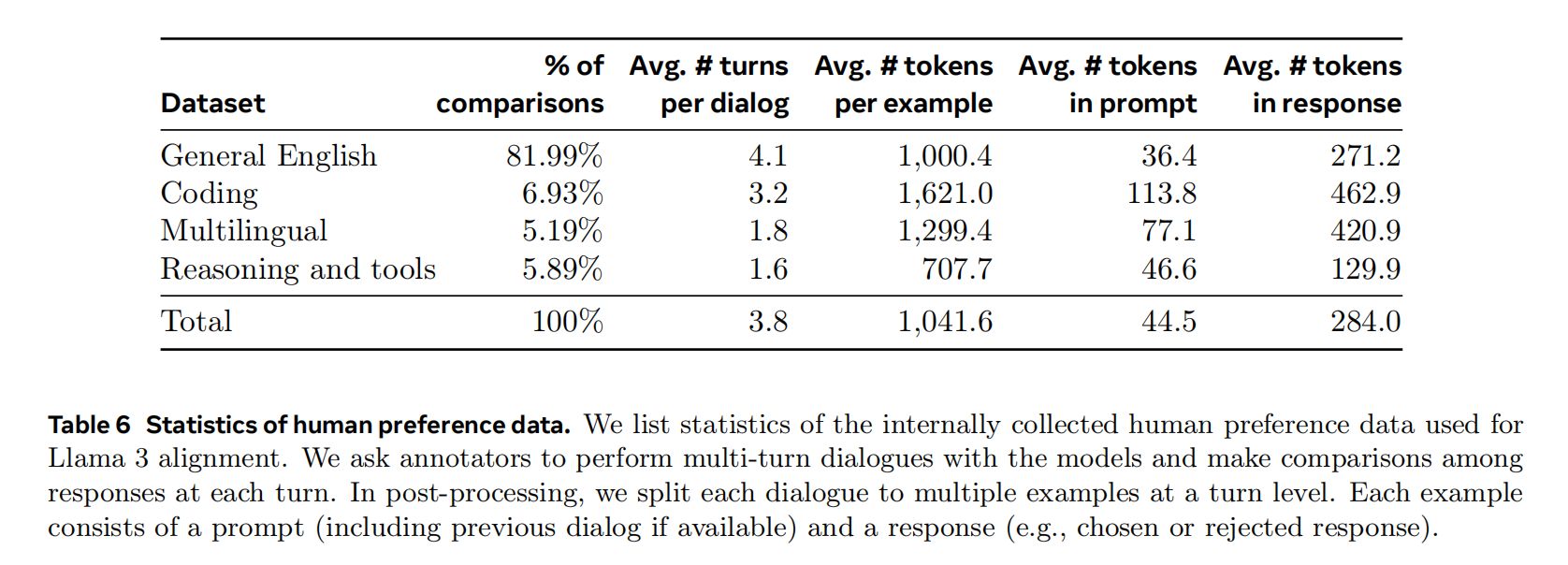
Learning rate 1e-5,训练 9K steps。SFT 的训练集中,有 21.9% 的数据是用于推理和工具使用的:
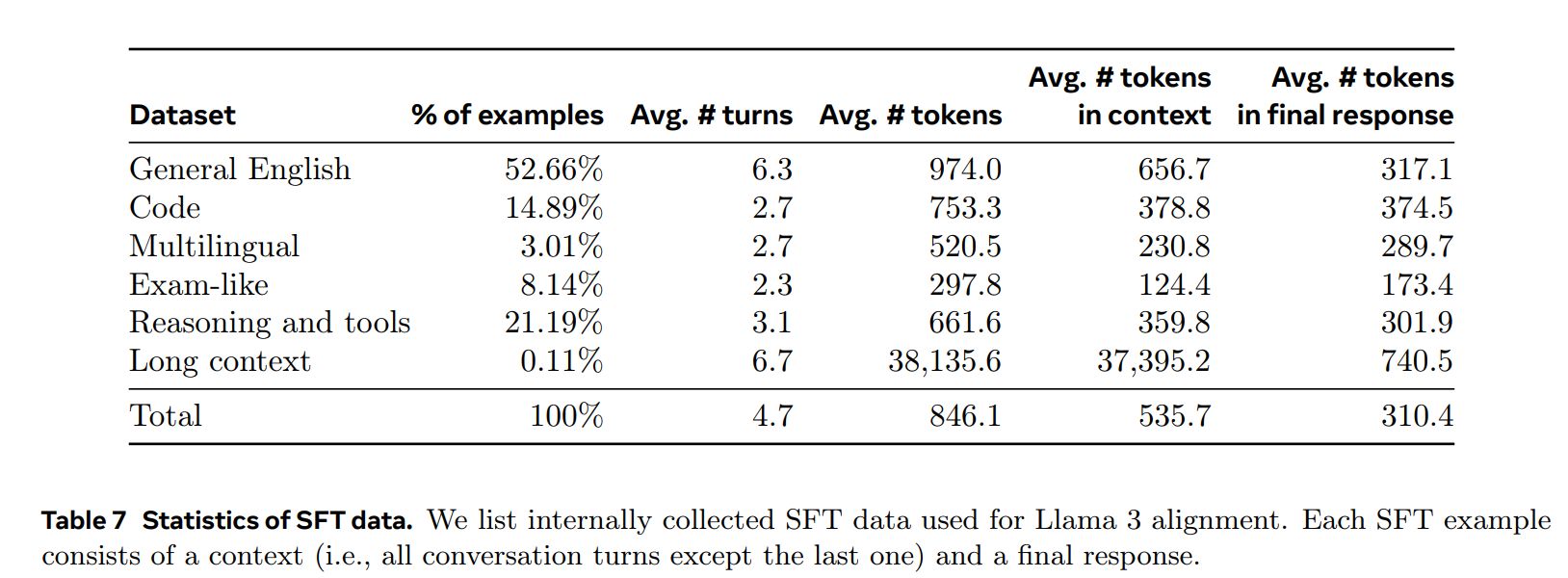
数据
参考 llama 3 herd of model 中对 SFT Tool 数据集的描述:
- 标注员只对 assistant 信息进行排名打分(通常模型对当前问题的推理能力越强,打分越高),不对 tool message 进行排名打分。
- 不采用 rejection sampling,因为 llama 团队没有在后期的 tool 测评中观察到它带来的收益。
为了加快标注过程,llama 团队首先通过在之前的 Llama 3 检查点生成的合成数据上进行微调来引导基本的工具使用能力。因此,标注员需要进行的编辑较少。同样地,随着 Llama 3 在开发过程中逐渐改进,我们逐步复杂化人类标注协议:从标注单轮 tool use 的对话数据开始,逐步过渡到标注对话中包含了 tool use 的数据,最后到标注对话中包含了多步 tool use 以及数据分析的训练数据。
llama 团队采用了以下方法来构造 Synthetic Tool datasets
single-step tool use 数据
参考上文中提到的标注方案,llama 团队先构造了该数据集,并对模型进行单论 tool use 训练。构造步骤:
- 通过 few-shot,用模型生成用户 prompt。该 prompt 必须涉及到调用 1 个 llama 的核心工具(core tools)。
- 通过 few-shot,和 step 1 中的 prompt,生成对应的 tool call 回答(包括调用工具名称,对应参数)。
- 执行 step 2 中的工具和参数,得到对应的 tool output。
- 让模型基于 用户 prompt,tool call,tool output,生成最终回复。
因此整个数据集包括了:system prompt, user prompt, tool call, tool output 和 final answer。在获得数据集后,llama 还过滤了约 30% 的数据集,以去除无法执行工具或有其他格式问题的数据。
根据 llama 报告中介绍 core tools 包括 brave_search, wolfram_alpha, and code interpreter 等 python 对象。
Multi-step tool use 数据:
Multi-step 与 single step 的 tool use 数据生成方式相似:
- 通过 few-shot,用模型生成用户 prompt。该 prompt 必须是一个需要使用多个 tool 来获得答案的任务(这些 tool 不一定得从 core tool 中选)。
- 基于 step 1 的 prompt,让 llama 3 生成包含了推理步骤和对应 tool call 信息的数据,具体可以看下图:
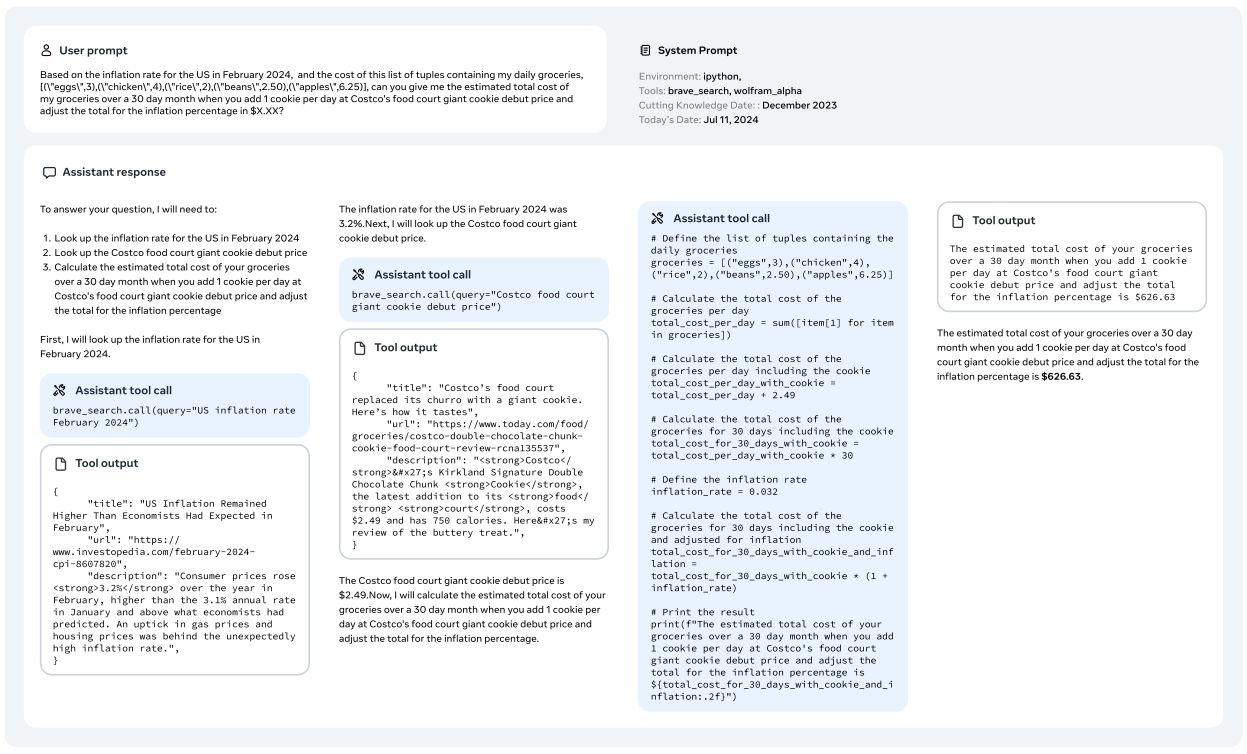
File uploads 数据:
File Uploads 数据参考下图训练数据示例。prompt 都是基于某个文件进行提问,问题包括总结,查找 bug,优化某个部分,数据分析等操作。
除此外,llama 在 system prompt 中进行了调试,让模型能够只在激活了 tool call 的情况下去调用共外部工具。
llama 团队采用了以下方法来构造 Zero-shot tool use data (与 function calling 类似)
Single, nested, and parallel function calling: Calls can be simple, nested, i.e. we pass a function call as an argument of another function, or parallel, i.e. the model returns a list of independent function calls. Generating a diverse set of functions, queries and ground truths can be challenging (Mekala et al., 2024), and we resort to mining the Stack (Kocetkov et al., 2022) to ground our synthetic user queries in real functions. More precisely, we extract function calls and their definitions, clean and filter them, e.g. for missing docstrings or non-executable functions, and use Llama 3 to generate a natural language query corresponding to the function call. 以上为原文描述,个人理解是 llama 基于 the Stack 的开源数据进行筛选/修改,构造了 function call 信息,而后用 llama 3 基于 function call 信息,生成对应的用户 query。
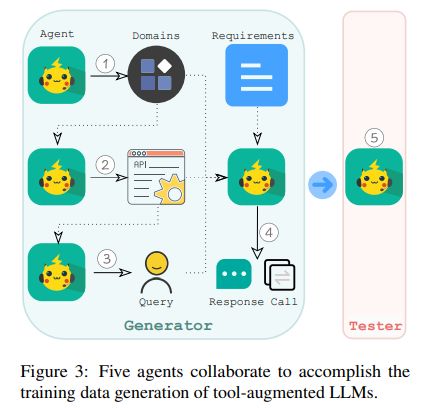
Multi-turn function calling: 采用了 API-Bank: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Tool-Augmented LLMs 中的方法生成数据。Llama 采用了 5 个 agent 如下图:
第一个 agent 用于生成不同的领域,如医疗保险,健身等。
第二个 agent,根据领域数据,生成潜在的 API。值得注意的是,在这一阶段,为了确保模拟 API 的真实性,我们在代理输入中加入了来自公共 API 的示例。
第三个 agent 从模拟 API 中随机选择一个或多个 API。此外,它还选择了我们设计原则中概述的一种能力。然后使用这些信息创建一个匹配所选能力的 query 问题,这个 query 问题可以通过调用所选 API 来完成回答。
第四个 agent 将领域、API、能力和 query 作为输入。这个 agent 需要通过模拟的方式调用选择的 API,然后根据 API 结果生成 response。
最后,我们引入了第五个 agent,作为测试者。该 agent 自动验证生成的数据是否符合我们的设计原则(实际上它丢弃了 35% 的实例)
所有的 agent 都是通过简单的 prompt + llama 3 实现。
DPO
Llama 发现 PPO 没有 DPO 好,于是只用了 DPO,preference data 中,有 5.89% 是和 reasoning 还有 tool 相关的。
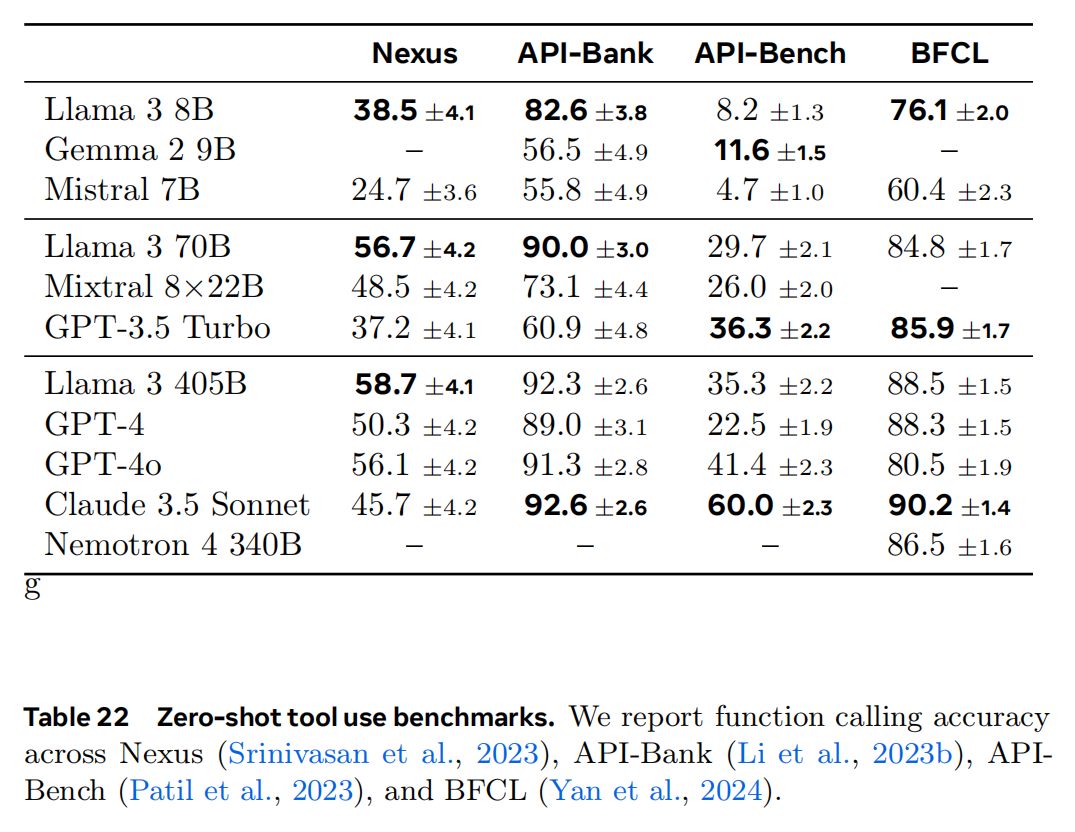
效果
Llama 的工具调用能力还是不错的:
其他
更多关于 llama 3.1 tool 和 reasoning 的细节,推荐查看 The Llama 3 Herd of Models。
Mistral Large 2
Mistral Large 也是采用了额外的 special token 来辅助 function call 的处理。
比如对于以下对话内容:
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in Paris?"},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "","tool_calls": [
{"type": "function","id":'D681PevKs',"function":
{"name": "get_current_weather", "arguments": {"location": "Paris, France", "format": "celsius"}}
}]},
{"role":"tool", "name":"get_current_weather", "content":"20", "tool_call_id":'D681PevKs'}
]
经过 mistral large 2 的 tokenizer 处理:
def get_current_weather(location: str, format: str):
"""
Get the current weather
Args:
location: The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA
format: The temperature unit to use. Infer this from the users location. (choices: ["celsius", "fahrenheit"])
"""
pass
model_path = "/home/kevin/models/Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path,
trust_remote_code=True,
)
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages,
tokenize=False,
tools = [get_current_weather],
add_generation_prompt=True)
输入 input 如下:
<s>[AVAILABLE_TOOLS] [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA"
},
"format": {
"type": "string",
"enum": [
"celsius",
"fahrenheit"
],
"description": "The temperature unit to use. Infer this from the users location."
}
},
"required": [
"location",
"format"
]
}
}
}
]
[/AVAILABLE_TOOLS]
[INST] What's the weather like in Paris?[/INST]
[TOOL_CALLS]
[
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"arguments": {
"location": "Paris, France",
"format": "celsius"
},
"id": "D681PevKs"
}
]
</s>
[TOOL_RESULTS] {"content": 20, "call_id": "D681PevKs"}[/TOOL_RESULTS]
关注点:
- 为了方便展示观看,以上
inputs进行了必要的格式化。 - function 的信息是统一放在了 system prompt 的地方。
- 用了
[TOOL_CALLS],[TOOL_RESULTS]等额外 token 来辅助 function calling。
具体的 mistral large 2 Chat Template 如下:
{%- if messages[0]["role"] == "system" %}
{%- set system_message = messages[0]["content"] %}
{%- set loop_messages = messages[1:] %}
{%- else %}
{%- set loop_messages = messages %}
{%- endif %}
{%- if not tools is defined %}
{%- set tools = none %}
{%- endif %}
{%- set user_messages = loop_messages | selectattr("role", "equalto", "user") | list %}
{%- for message in loop_messages | rejectattr("role", "equalto", "tool") | rejectattr("role", "equalto", "tool_results") | selectattr("tool_calls", "undefined") %}
{%- if (message["role"] == "user") != (loop.index0 % 2 == 0) %}
{{- raise_exception("After the optional system message, conversation roles must alternate user/assistant/user/assistant/...") }}
{%- endif %}
{%- endfor %}
{{- bos_token }}
{%- for message in loop_messages %}
{%- if message["role"] == "user" %}
{%- if tools is not none and (message == user_messages[-1]) %}
{{- "[AVAILABLE_TOOLS] [" }}
{%- for tool in tools %}
{%- set tool = tool.function %}
{{- '{"type": "function", "function": {' }}
{%- for key, val in tool.items() if key != "return" %}
{%- if val is string %}
{{- '"' + key + '": "' + val + '"' }}
{%- else %}
{{- '"' + key + '": ' + val|tojson }}
{%- endif %}
{%- if not loop.last %}
{{- ", " }}
{%- endif %}
{%- endfor %}
{{- "}}" }}
{%- if not loop.last %}
{{- ", " }}
{%- else %}
{{- "]" }}
{%- endif %}
{%- endfor %}
{{- "[/AVAILABLE_TOOLS]" }}
{%- endif %}
{%- if loop.last and system_message is defined %}
{{- "[INST] " + system_message + "\n\n" + message["content"] + "[/INST]" }}
{%- else %}
{{- "[INST] " + message["content"] + "[/INST]" }}
{%- endif %}
{%- elif message["role"] == "tool_calls" or message.tool_calls is defined %}
{%- if message.tool_calls is defined %}
{%- set tool_calls = message.tool_calls %}
{%- else %}
{%- set tool_calls = message.content %}
{%- endif %}
{{- "[TOOL_CALLS] [" }}
{%- for tool_call in tool_calls %}
{%- set out = tool_call.function|tojson %}
{{- out[:-1] }}
{%- if not tool_call.id is defined or tool_call.id|length != 9 %}
{{- raise_exception("Tool call IDs should be alphanumeric strings with length 9!") }}
{%- endif %}
{{- ', "id": "' + tool_call.id + '"}' }}
{%- if not loop.last %}
{{- ", " }}
{%- else %}
{{- "]" + eos_token }}
{%- endif %}
{%- endfor %}
{%- elif message["role"] == "assistant" %}
{{- " " + message["content"] + eos_token}}
{%- elif message["role"] == "tool_results" or message["role"] == "tool" %}
{%- if message.content is defined and message.content.content is defined %}
{%- set content = message.content.content %}
{%- else %}
{%- set content = message.content %}
{%- endif %}
{{- '[TOOL_RESULTS] {"content": ' + content|string + ", " }}
{%- if not message.tool_call_id is defined or message.tool_call_id|length != 9 %}
{{- raise_exception("Tool call IDs should be alphanumeric strings with length 9!") }}
{%- endif %}
{{- '"call_id": "' + message.tool_call_id + '"}[/TOOL_RESULTS]' }}
{%- else %}
{{- raise_exception("Only user and assistant roles are supported, with the exception of an initial optional system message!") }}
{%- endif %}
{%- endfor %}
glm-4-9b-chat
对话协议
GLM 中的特殊 token 有:
["<|endoftext|>", "[MASK]", "[gMASK]", "[sMASK]", "<sop>", "<eop>", "<|system|>",
"<|user|>", "<|assistant|>", "<|observation|>", "<|begin_of_image|>", "<|end_of_image|>",
"<|begin_of_video|>", "<|end_of_video|>"]
其中 <|observation|> 用来标记工具的执行结果。
GLM 使用的 chat template 如下:
[gMASK]<sop>{% for item in messages %}{% if item['tools'] is defined %}<|system|>
你是一个名为 GLM-4 的人工智能助手。你是基于智谱 AI 训练的语言模型 GLM-4 模型开发的,你的任务是针对用户的问题和要求提供适当的答复和支持。
# 可用工具{% set tools = item['tools'] %}{% for tool in tools %}{% if tool['type'] == 'function' %}
## {{ tool['function']['name'] }}
{{ tool['function'] | tojson(indent=4) }}
在调用上述函数时,请使用 Json 格式表示调用的参数。{% elif tool['type'] == 'python' %}
## python
当你向 `python` 发送包含 Python 代码的消息时,该代码将会在一个有状态的 Jupyter notebook 环境中执行。
`python` 返回代码执行的输出,或在执行 60 秒后返回超时。
`/mnt/data` 将会持久化存储你的文件。在此会话中,`python` 无法访问互联网。不要使用 `python` 进行任何网络请求或者在线 API 调用,这些在线内容的访问将不会成功。{% elif tool['type'] == 'simple_browser' %}
## simple_browser
你可以使用 `simple_browser` 工具。该工具支持以下函数:
`search(query: str, recency_days: int)`:使用搜索引擎进行查询并显示结果,可以使用 `recency_days` 参数控制搜索内容的时效性。
`mclick(ids: list[int])`:获取一系列指定 id 的页面内容。每次调用时,须选择 3-10 个页面。选择多个角度的页面,同时尽可能选择可信任的信息来源。考虑到部分页面是无法加载的,你也可以多打开一些可能有用的页面而不用担心内容过多。
`open_url(url: str)`:打开指定的 URL。
使用 `【{引用 id}†{引用文本}】` 来引用内容。
操作步骤:1. 使用 `search` 来获得信息列表; 2. 使用 `mclick` 来获取指定 ID 页面的内容; 3. 根据获得的内容进行回复。在回复中应当引用信息来源。
如果用户提供了 URL,也可以用 `open_url` 直接打开页面。
如果初次搜索结果没有找到合适的信息,也可以再次使用 `search` 进行搜索。{% elif tool['type'] == 'cogview' %}
## cogview
如果用户的请求中包含了对图像的描述,你可以使用 `cogview` 来生成图像并展示给用户。你需要向 `cogview` 发送图像描述,规则:
- 发送给 `cogview` 的消息必须使用英语。用户的中文描述必须完全翻译为英语。
- 应当尽可能详细地描述图像生成的需求,需求描述约 100 英文单词。
- 保持用户原始描述的意图。不要虚构内容或者没见过的人物。
- 如无特殊说明,所在地为中国,持有中国立场并遵循中国社会主义价值观。{% endif %}{% endfor %}{% endif %}{% if item['content'] %}<|{{ item['role'] }}|>{{ item['metadata'] }}
{{ item['content'] }}{% endif %}{% endfor %}{% if add_generation_prompt %}<|assistant|>{% endif %}
通过以下对话内容进行示例:
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "",
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_recommended_books",
"description": "Get recommended books based on user's interests",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"interests": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"description": "The interests to recommend books for"
}
},
"required": [
"interests"
]
}
}
}
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Hi, I am looking for some book recommendations. I am interested in history and science fiction."
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "{\"name\": \"get_recommended_books\", \"arguments\": {\"interests\": [\"history\", \"science fiction\"]}}"
},
{
"role": "observation",
"content": "{\"books\": [\"Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind by Yuval Noah Harari\", \"A Brief History of Time by Stephen Hawking\", \"Dune by Frank Herbert\", \"The Martian by Andy Weir\"]}"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Based on your interests in history and science fiction, I would recommend the following books: \"Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind\" by Yuval Noah Harari, \"A Brief History of Time\" by Stephen Hawking, \"Dune\" by Frank Herbert, and \"The Martian\" by Andy Weir."
}
]
那么,对应的 input 就会是:
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("/home/kevin/models/glm-4-9b-chat", trust_remote_code=True)
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages,
tokenize=False)
# inputs =
"""
[gMASK]<sop><|system|>
你是一个名为 GLM-4 的人工智能助手。你是基于智谱 AI 训练的语言模型 GLM-4 模型开发的,你的任务是针对用户的问题和要求提供适当的答复和支持。
# 可用工具
## get_recommended_books
{
"name": "get_recommended_books",
"description": "Get recommended books based on user's interests",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"interests": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"description": "The interests to recommend books for"
}
},
"required": [
"interests"
]
}
}
在调用上述函数时,请使用 Json 格式表示调用的参数。<|user|>
Hi, I am looking for some book recommendations. I am interested in history and science fiction.<|assistant|>
{"name": "get_recommended_books", "arguments": {"interests": ["history", "science fiction"]}}<|observation|>
{"books": ["Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind by Yuval Noah Harari", "A Brief History of Time by Stephen Hawking", "Dune by Frank Herbert", "The Martian by Andy Weir"]}<|assistant|>
Based on your interests in history and science fiction, I would recommend the following books: "Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind" by Yuval Noah Harari, "A Brief History of Time" by Stephen Hawking, "Dune" by Frank Herbert, and "The Martian" by Andy Weir.
"""
效果
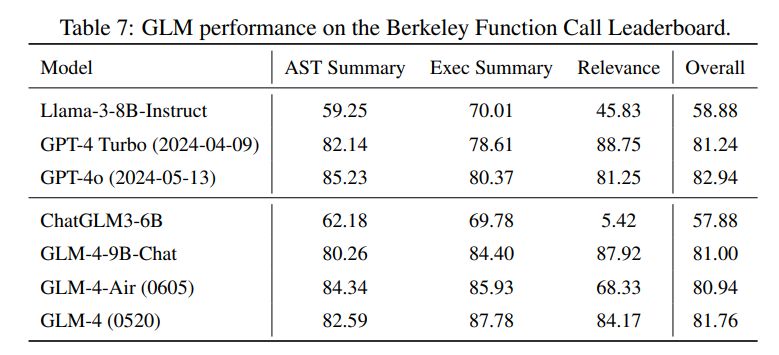
GLM function call 能力(Berkeley function-calling leaderboard):
其他
GLM 公开的信息还是挺少的,官方 github 及 官方技术报告 都没有找到一些 function call 训练细节。
Qwen 2
参考 Qwen2 的这个 function calling 文档。Qwen 2 的 function calling 功能需要依靠 Qwen-Agent 来实现。
Qwen2 instruct 的 chat template 如下:
{% for message in messages %}{% if loop.first and messages[0]['role'] != 'system' %}{{ '<|im_start|>system
You are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>
' }}{% endif %}{{'<|im_start|>' + message['role'] + '
' + message['content'] + '<|im_end|>' + '
'}}{% endfor %}{% if add_generation_prompt %}{{ '<|im_start|>assistant
' }}{% endif %}
可以看到,chat template 中是没有 tool 相关的 special token 的。
参考 Qwen-Agent 的 BaseFnCallModel 实现(github link),当用 Qwen2 官方示例的 function call 方式时,function 的信息会被添加到 system prompt 中:
def _prepend_fncall_system(
self,
messages: List[Message],
functions: List[Dict],
lang: Literal['en', 'zh'],
parallel_function_calls: bool = False,
) -> List[Message]:
tool_desc_template = FN_CALL_TEMPLATE[lang + ('_parallel' if parallel_function_calls else '')]
tool_descs = '\n\n'.join(get_function_description(function, lang=lang) for function in functions)
tool_names = ','.join(function.get('name', function.get('name_for_model', '')) for function in functions)
tool_system = tool_desc_template.format(tool_descs=tool_descs, tool_names=tool_names)
assert messages[0].role == SYSTEM
messages = copy.deepcopy(messages[:1]) + messages[1:]
if isinstance(messages[0].content, str):
messages[0].content += '\n\n' + tool_system
else:
messages[0].content.append(ContentItem(text='\n\n' + tool_system))
return messages
添加 function call 的模板有中文和英文模板,也有并行调用和非并行调用模板,具体可以在 Qwen-Agent 代码中查看,以下是一个中文模板示例:
"""# 工具
## 你拥有如下工具:
{tool_descs}
## 你可以在回复中插入零次、一次或多次以下命令以调用工具:
✿FUNCTION✿: 工具名称,必须是[{tool_names}]之一。
✿ARGS✿: 工具输入
✿RESULT✿: 工具结果
✿RETURN✿: 根据工具结果进行回复,需将图片用渲染出来"""
在得到模型输出之后,通过 Qwen-Agent 中的 _postprocess_fncall_message 来抽取对应的结构化数据。
其他
Qwen 初代的 function call 采用的 react 的思路,当时模型有在额外的工具调用数据集上专门对 function call 进行训练。Qwen 2 Qwen2 Technical Report, blog 中虽然没有提到 function call 实现细节,但个人猜测也是经过了额外的 function call 能力训练。