论文笔记 | 探索 LLM 的上下文长度外推
大模型上下文在前段时间有点火,TODO 里堆积的论文也越来越多(。
本文记录了 LLM 在长度外推方面的文章笔记,包括位置编码相关的 ALiBi 、 ROPE 和 线性插值(PI) , NTK ;注意力相关的 GQA , SWA , LM-INFINITE , StreamingLLM ;以及 meta 的综述 Effective Long-Context Scaling of Foundation Models 记录。
位置编码
ALIBI: TRAIN SHORT, TEST LONG: ATTENTION WITH LINEAR BIASES ENABLES INPUT LENGTH EXTRAPOLATION
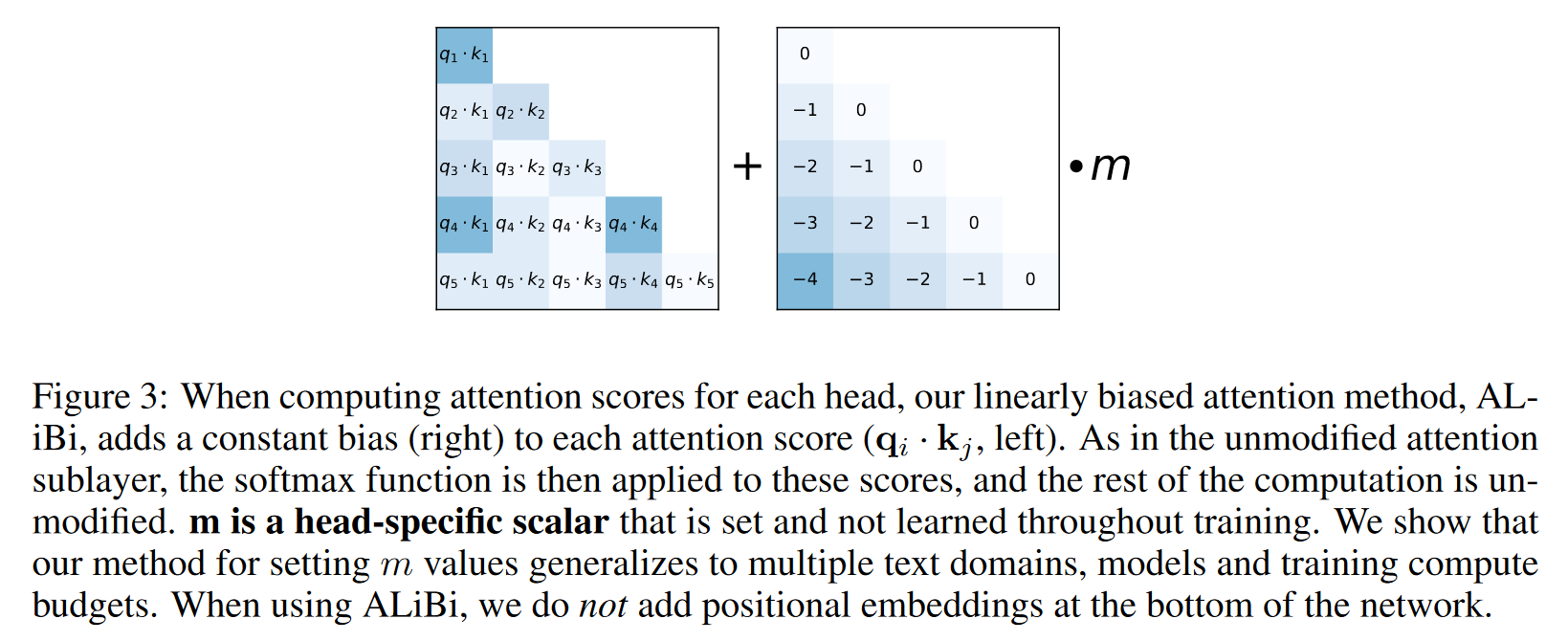
将原先的 attention score 计算方式改为:
其中 为超参数。从下图可以看出,ALiBi 限定了注意力的范围。
ROPE: Rotary Position Embedding
对比 Transformer 绝对位置编码,ROPE 通过将向量以复数方式推理, 巧妙地实现了以添加绝对位置编码的方式,在 attention 中计算了相对位置信息。关于 ROPE 详细可以参考笔者的另一篇笔记:
https://kevinng77.github.io/posts/notes/articles/%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0rope.html
Extending Context Window of Large Language Models via Positional Interpolation
文中提出一种 Linear 的 position Interpolation (线性内插)方案,该方案可以使得原先上下文长度为 2000 左右的 llama 模型,再仅通过 1000 steps 的微调之后,获得 32768 的窗口长度。并且在原先 2000 窗口长度的任务上,不会降低模型回复质量。具体方法是将 ROPE 替换为:
其中 为目标的 context window 大小,比如我们希望模型 context window 大小为 4096,那么 ROPE 的转变如下图:
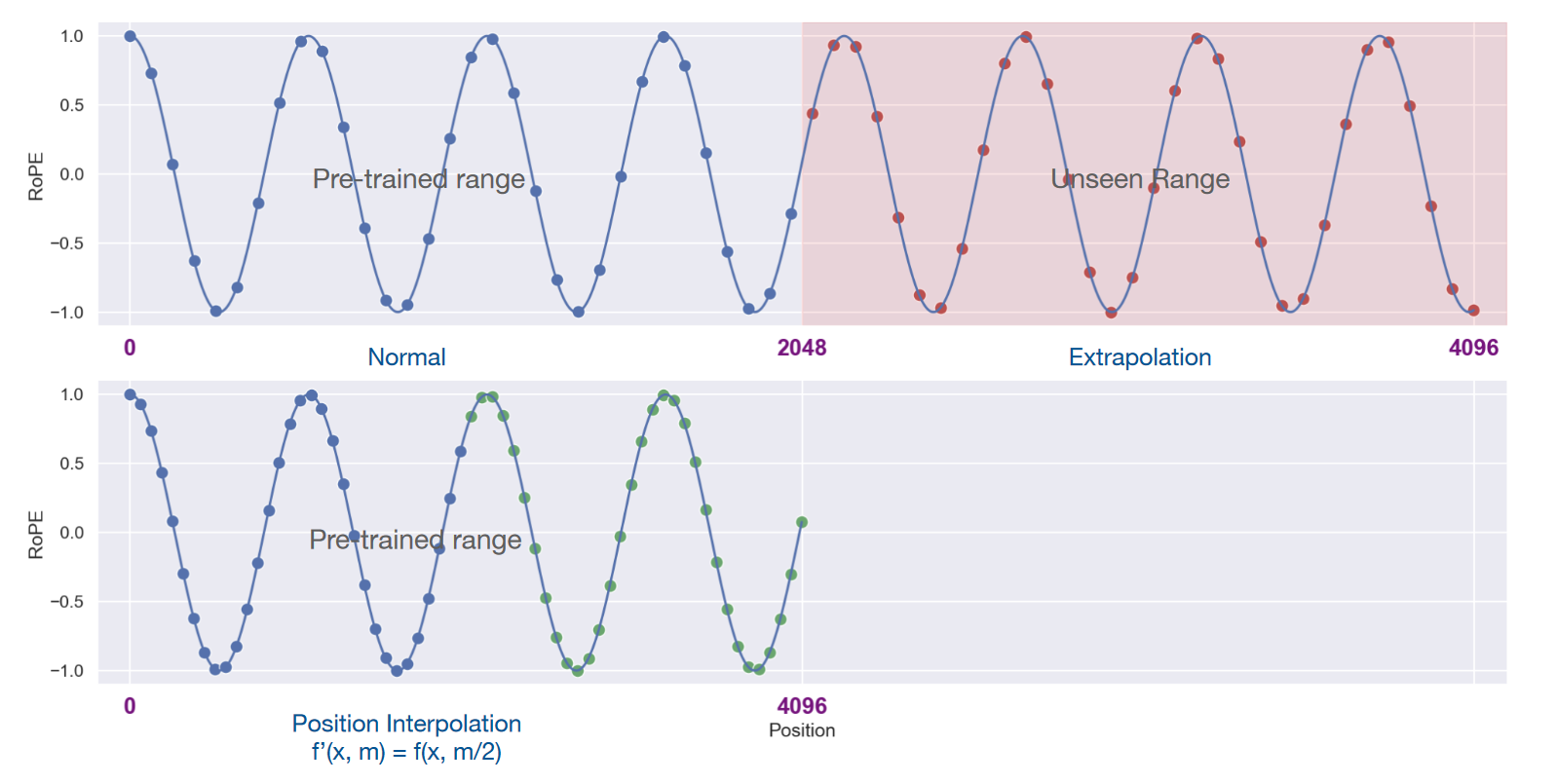
除了 position embedding 的变换,还需要使用 next token prediction 进行额外的微调来确保模型的效果。
相对于前一篇文中使用的线性插值,Neural Tangent Kerne 通过非线性插值方案,改变 RoPE 的 base,可以取得更好的效果。
提出 NTK 的网友也提供了对应的代码,核心部分即更改 RoPE 的 base:
import transformers
old_init = transformers.models.llama.modeling_llama.LlamaRotaryEmbedding.__init__
def ntk_scaled_init(self, dim, max_position_embeddings=2048, base=10000, device=None):
#The method is just these three lines
max_position_embeddings = 16384
a = 8 #Alpha value
base = base * a ** (dim / (dim-2)) #Base change formula
old_init(self, dim, max_position_embeddings, base, device)
该方案也在后续逐渐在 LLM 上被采用,如 Code Llama: Open Foundation Models for Code 。
Transformer 注意力的优化
GQA: Training Generalized Multi-Query Transformer Models from Multi-Head Checkpoints
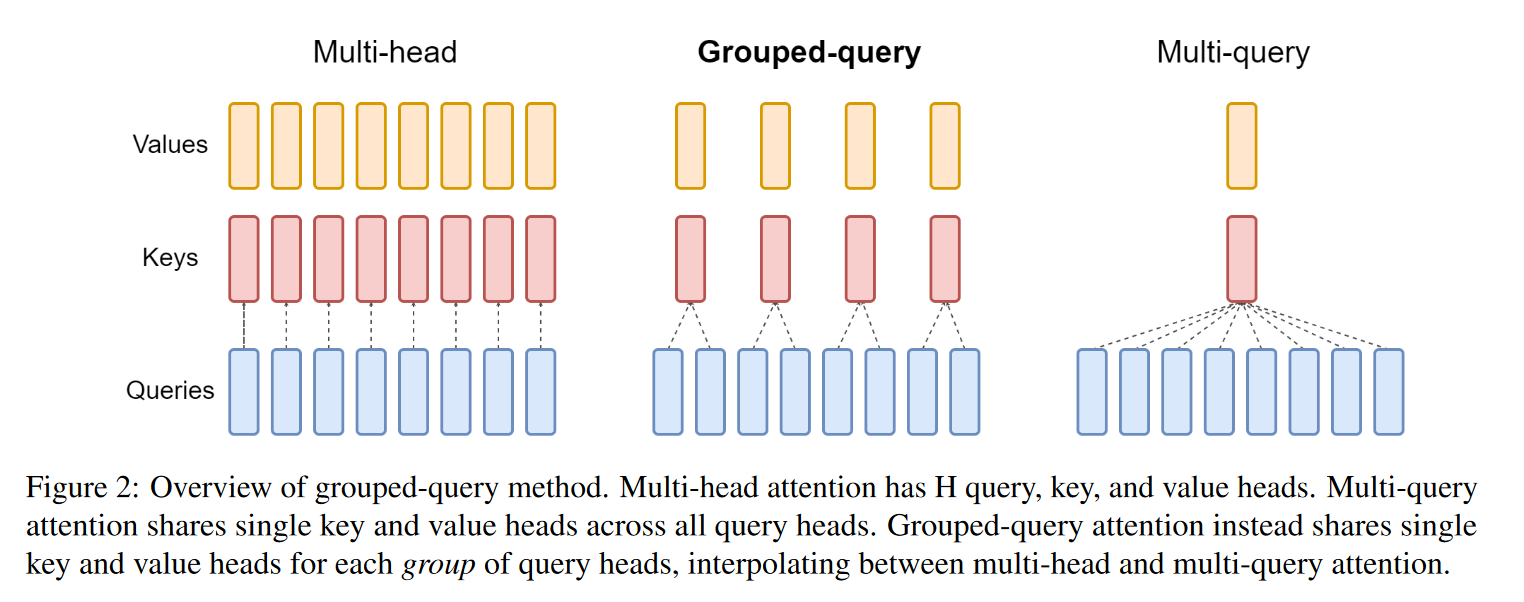
grouped-query attention 指出,Multi-Query Attention 提高了推理速度的同时,却可能极大地降低回复质量。因此根据上图,GQA 在推理速度和质量之间作了权衡。
以下为 GQA 文中的实验结果,值得注意的是论文中使用原 MHA checkpoint 转换为 GQA 权重后,还进行了额外的预训练:
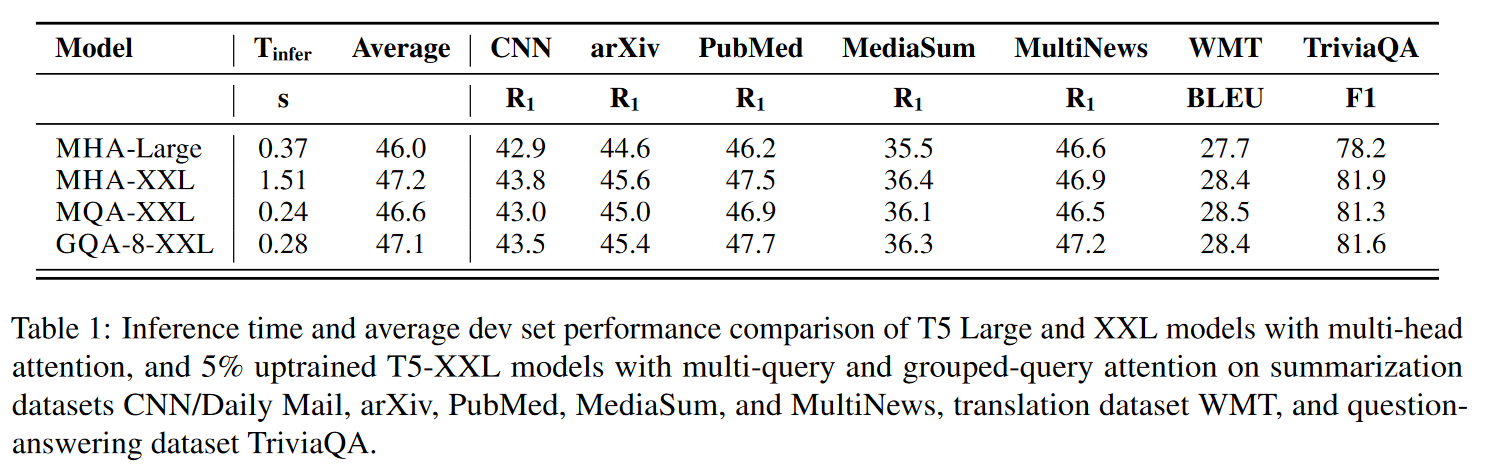
此外 Mistral,Llama2 的部分模型使用 GQA 时,采用的 kv head 数量似乎都是 8。
为什么现在大家都在用 MQA 和 GQA? 文中提到 MQA 和 GQA 能获得巨大加速的一个点在于:GPU 内存强的限制。由于 MQA 和 GQA 都降低了内存中数据的读取量,减少了计算单元的等待时间,因此推理速度的提高比想象中的要快更多。
Sliding Window Attention
以 Mistral 的 SWA 为例,Mistral 采用的 window size 为 4096,而后一共有 32 层 layer,那么采用 SWA 之后,理论上在进行 attention 的时候,可以收集到约 131K tokens 的信息。
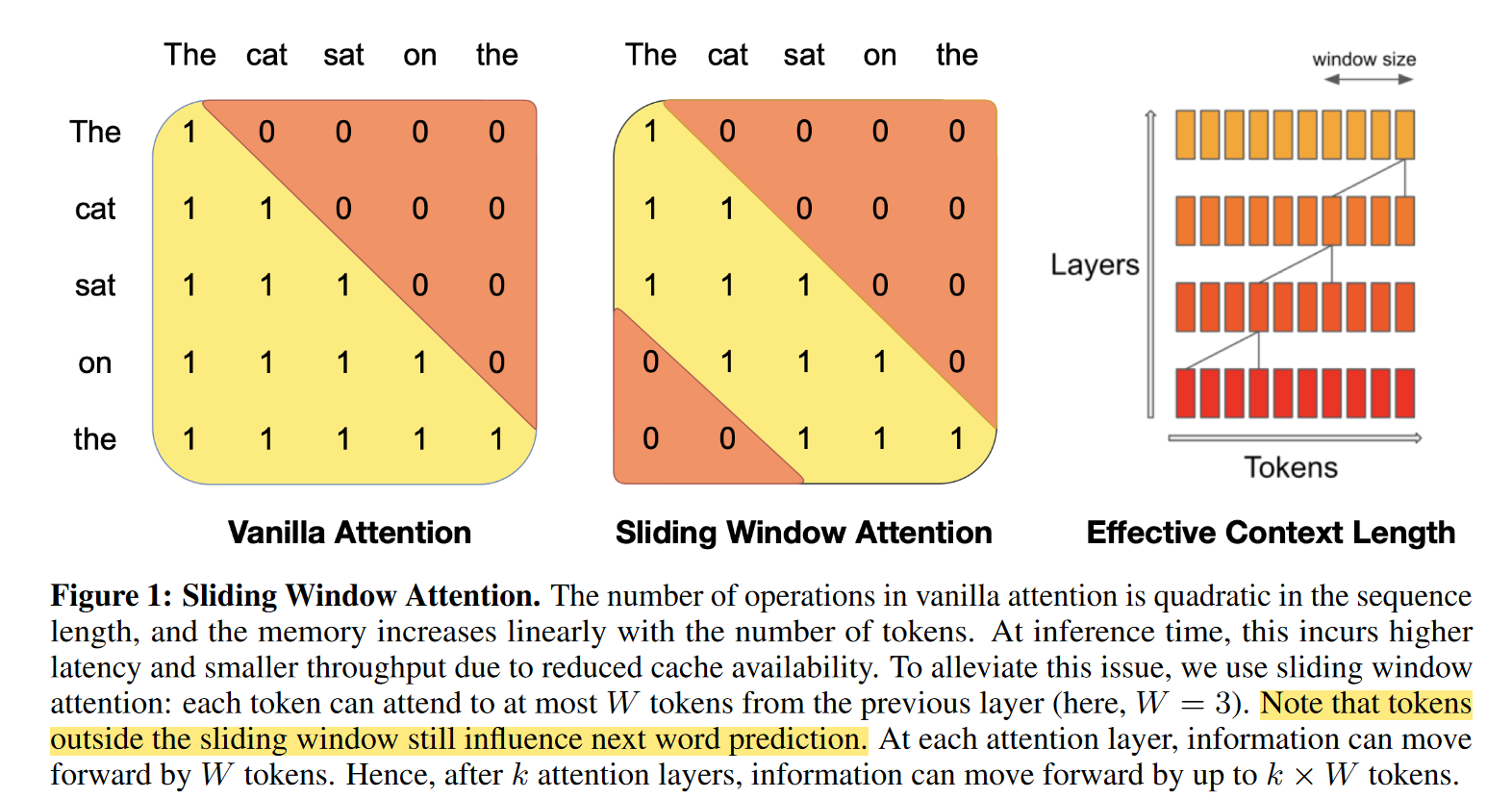
由于代用了固定的 attention 窗口大小,因此我们只需要一个大小为 W=window size 的 cache ,在计算第 i 个 token 的 cache 的时候,只需要覆盖 cache 中 i mod M 位置上的 hidden state 即可。
LM-INFINITE: SIMPLE ON-THE-FLY LENGTH GENERALIZATION FOR LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS
文中讨论了导致长度外推失败的几个因素:
UNSEEN DISTANCES
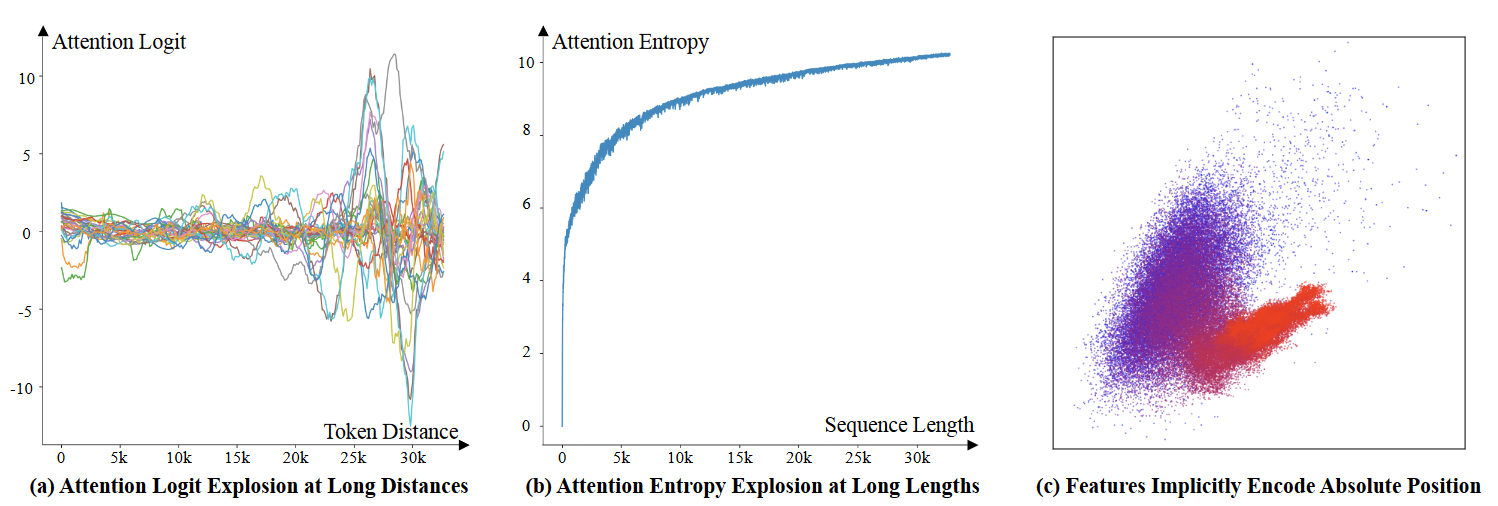
直观上来说推理时候的长度,远超出了训练集的长度,那么采样的效果一定不好。文中也证明了,随着长度的增加,如果我们要区分出新的 距离因素 ,那么,注意力的 logit 就必须增长到无限大。
UNSEEN NUMBER OF TOKENS
即便我们不考虑距离因素,那么当推理长度增加时,attention score 的分布会趋于平坦,导致信息的丢失。论文也通过 Attention Entropy 会趋于无限大进行了观点验证。
IMPLICITLY-ENCODED ABSOLUTE POSITION
文中发现:即使在网络中没有明确编码绝对位置信息,注意力机制仍然能够隐式地编码它。
论文对 LLaMa 第一层的 hidden state 进行 PCA 后发现:在图 c 中,头部的 token 为蓝色点,尾部的 token 为红色点。尾部的 token 在空间分布上,已经逐渐地失去了区分性。
LM-INFINITE 方法
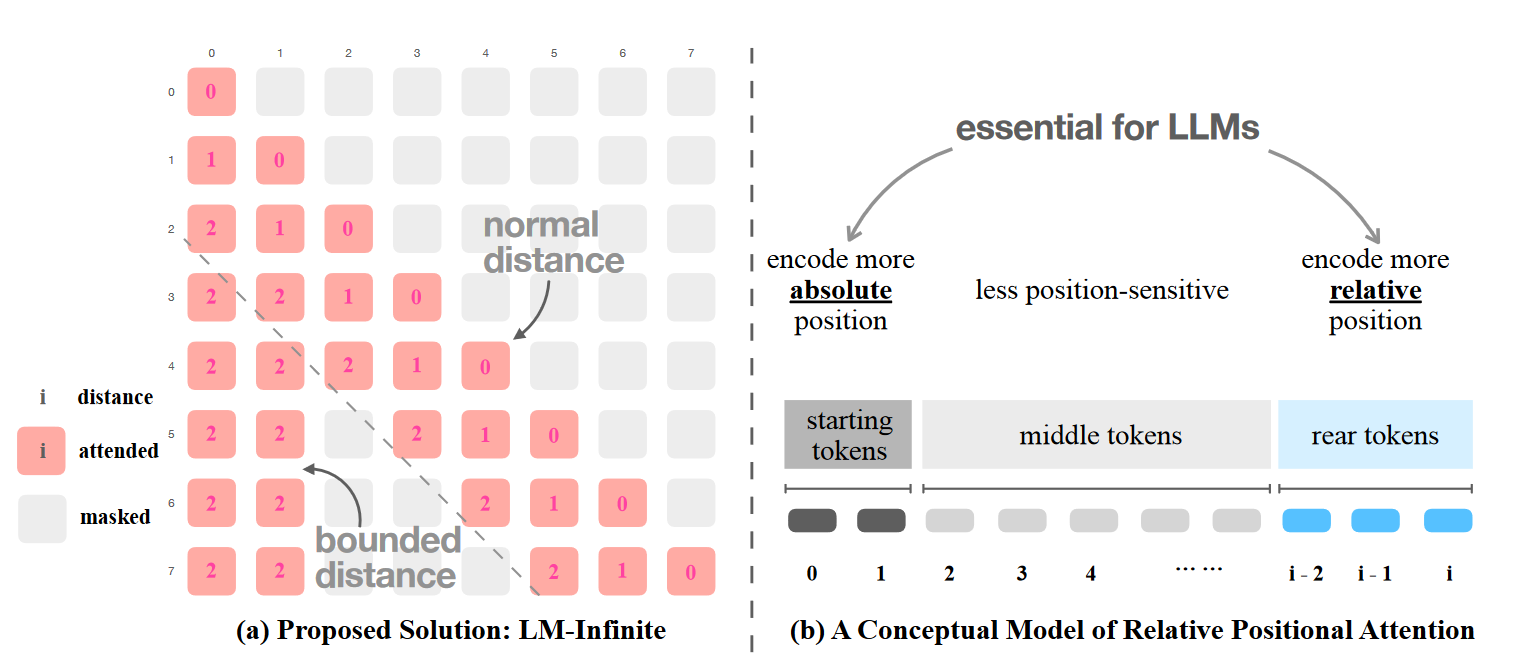
因此,LM-INFINITE 尝试了移动采样。对于注意力部分的计算,如果整个序列长度为 i 的话,那么我们只针对序列开始的 n_global 个 token 以及序列末尾的 n_local 个 token 进行注意力计算(参考上图 b 中的 start tokens 和 rear tokens 部分)。当 n_global=0 时,采样效果是非常差的。
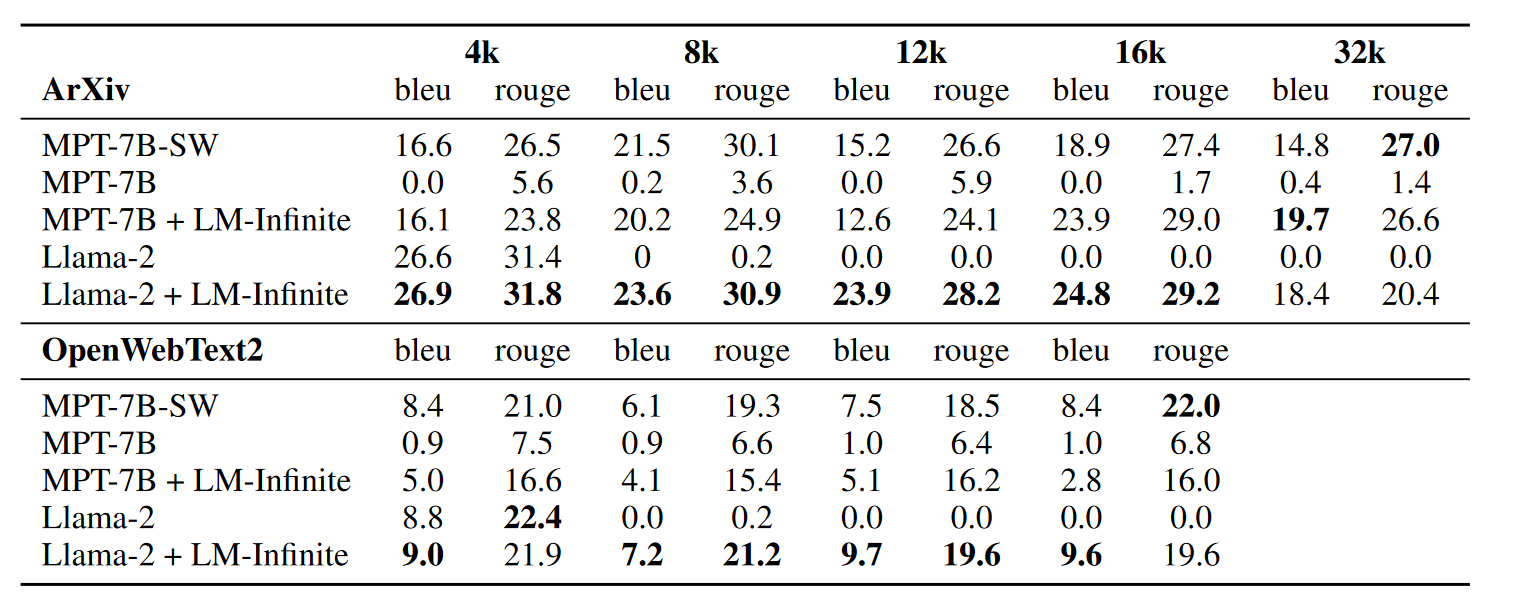
文中对采用了相对位置编码的主流模型(LlaMa, MPT, GPT),在 ArXiv 和 OpenWebText2 上计算了测试。
Perplexity 指标:
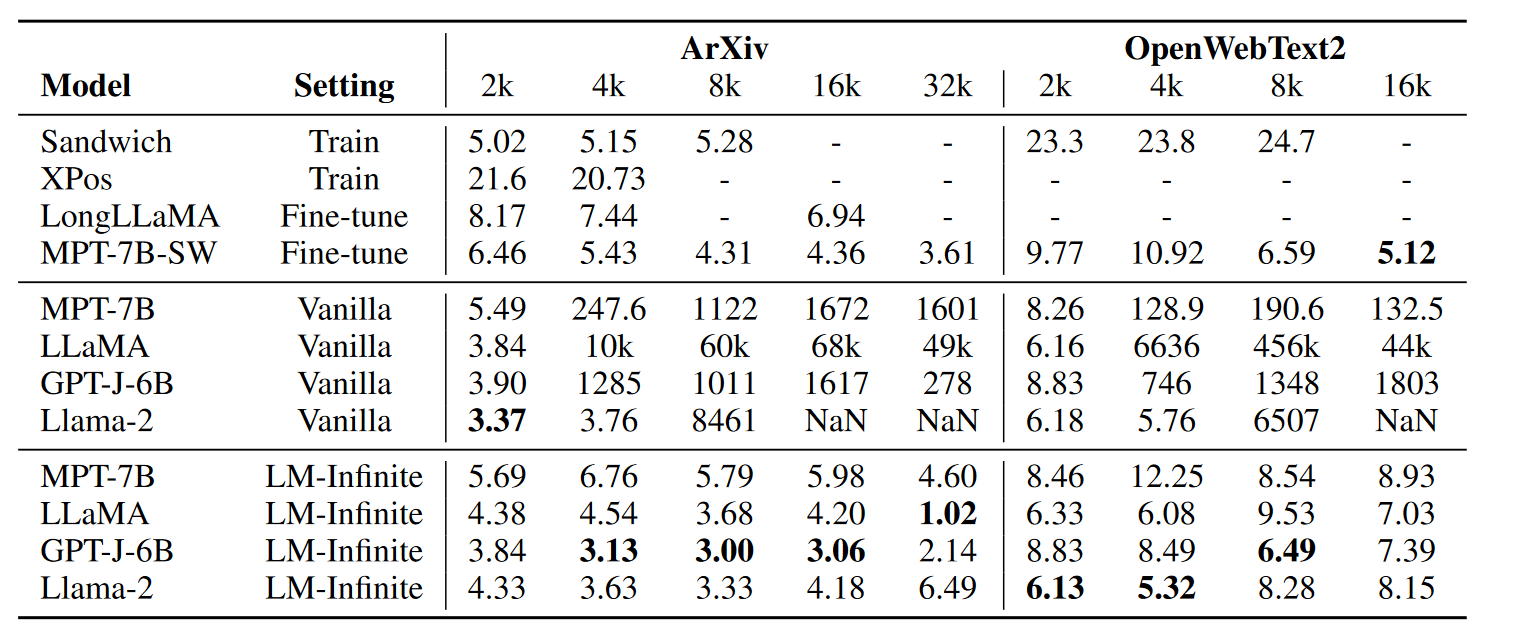
和 BLEU, ROUGE 指标:
StreamingLLM: EFFICIENT STREAMING LANGUAGE MODELS WITH ATTENTION SINKS
StreamingLLM 的想法与 LM-infinite 相似,在计算 attention 时候,只计算头部和尾部的 token,省略掉重点部分的 attention。
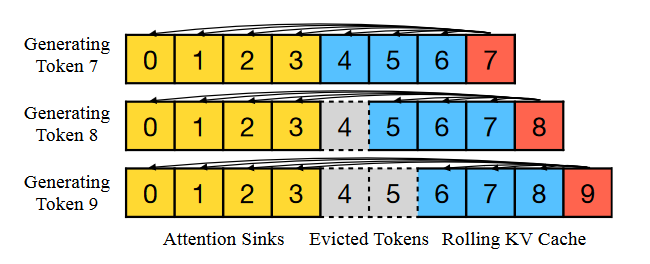
StreamingLLM 试验后提出,保留开头的 4 个 token 是个不错的选择。
在设置 position_id 时,输入的是连续不间断的 ID,如上图中,生成第 9 个 token 时,使用的 position id 为 [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
对于为什么开头的 tokens 不能从 KV 中去除,文中以下实验:
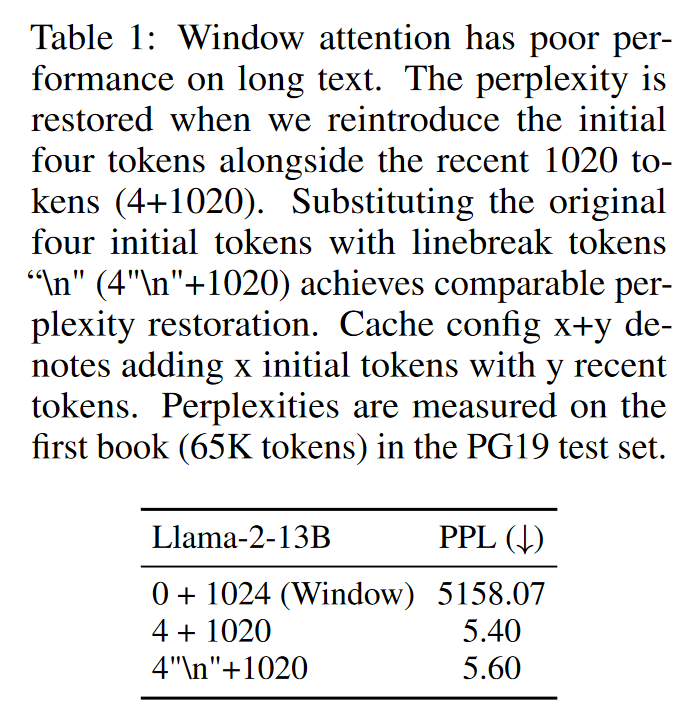
结果发现开头用 4 个 \n 替换原始文本后,PPL 增长了一点而已。
StreamLLM 官方仓库中特别指明:该方法并不会扩展上下文长度:
Can I input an extensive text, like a book, into StreamingLLM for summarization?
While you can input a lengthy text, the model will only recognize the latest tokens. Thus, if a book is an input, StreamingLLM might only summarize the concluding paragraphs, which might not be very insightful. As emphasized earlier, we neither expand the LLMs' context window nor enhance their long-term memory. StreamingLLM's strength lies in generating fluent text from recent tokens without needing a cache refresh.
LlaMA2 Long: Effective Long-Context Scaling of Foundation Models
Meta 提出的一篇对于扩展模型上下文能力的详细分析,主要讨论了长上下文模型的连续预训练方法、位置编码的设计、数据集的长度分布以及训练方案(Training Curriculum)对最终性能的影响。
方案:
首先进行额外的预训练,预训练过程中需要:
- 调整 position encoding 策略:meta 在实验中对 base 进行了调整,从 10000 改成了 500000。文中实验表示 RoPE ABF(adjusted base frequency,即仅对 base 进行修改)效果会好与下图中展示的其他方案。
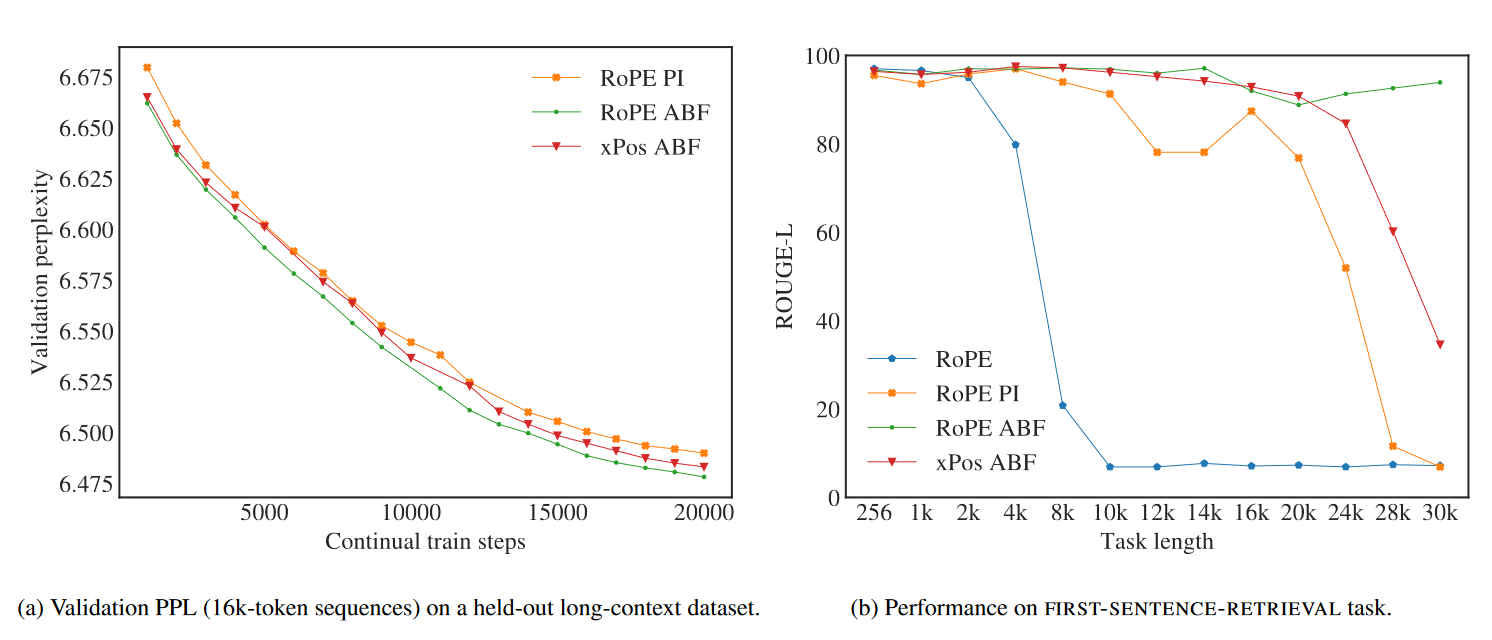
- 更换数据分布:Meta 表示对于长文本的预训练,数据的质量十分关键。并且一味地增加长文本的比重并不能持续地提高训练效果。
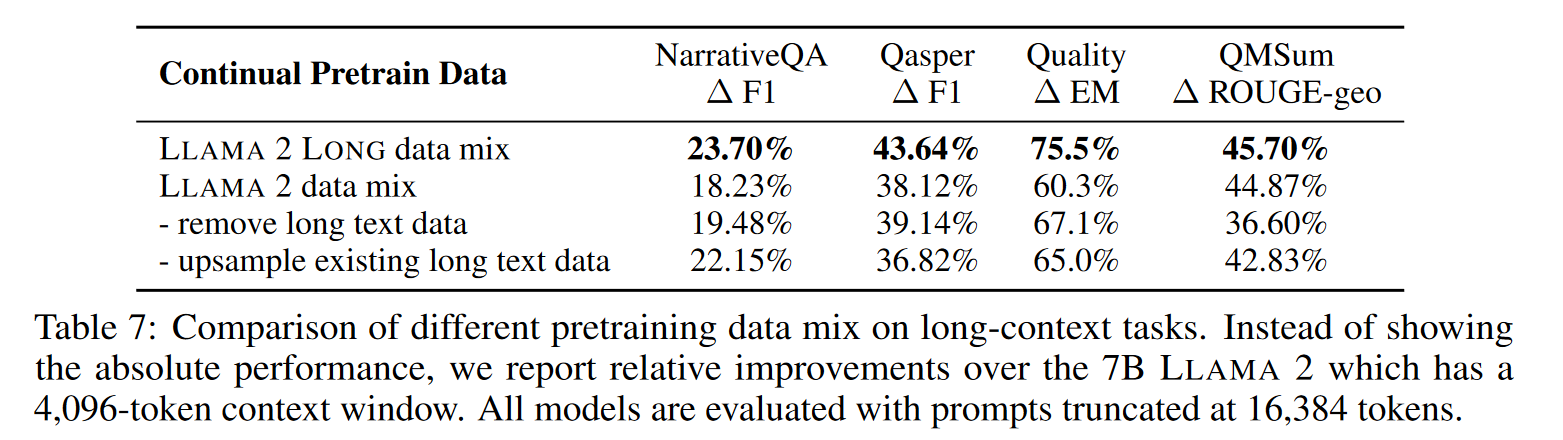
在下面地结果中展示了:即使我们在有限长度地文本下继续预训练,那么我们也能提高不少地模型效果。
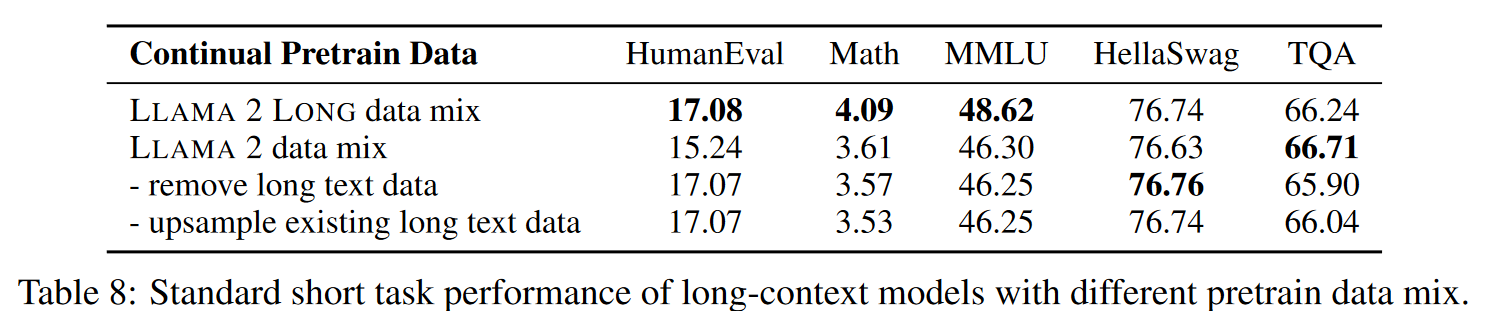
- 在优化过程中,采用了 FlashAttention,同时保持了与预训练时同样的 token per batch。对于 7/13B 模型采用 2e-5 学习率+ 2000 warm-up steps 的 cosine learning rate schedule.
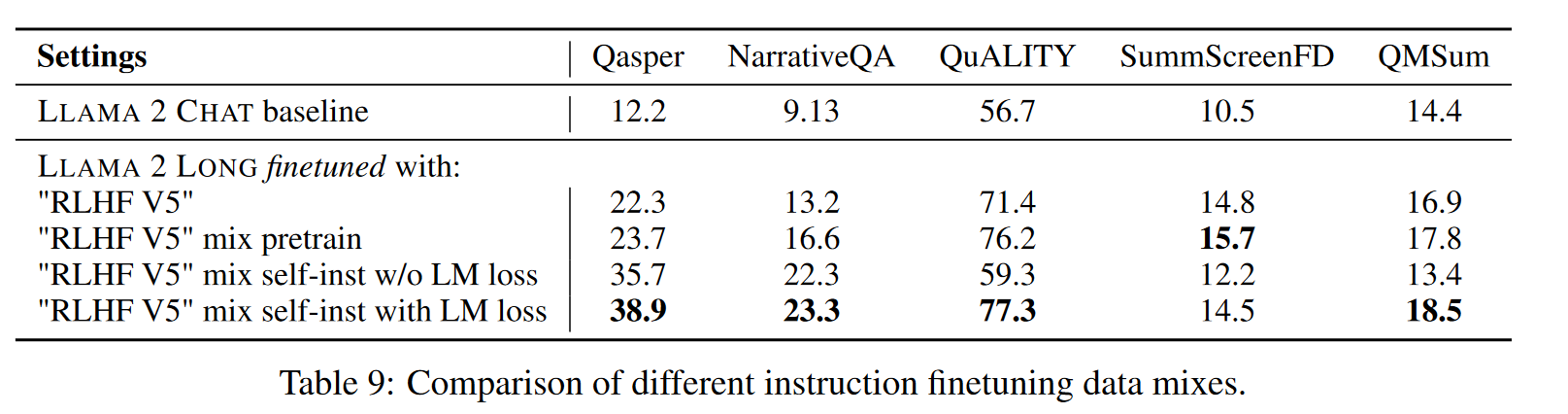
而后进行指令微调:
Meta 表示,指令微调环节主要关注点在于 QA 数据集的构造。文中先从预训练语料(似乎是 LLAMA 2 CHAT 用到的 RLHF 语料)中选出长文档,而后让 LLAMA 2 CHAT 生成一些 QA 训练对。同时用 LLAMA 2 CHAT 进行答案验证。
对于生成的训练数据,如果过短的话,会被 padding 到 16384 token。
训练方案:
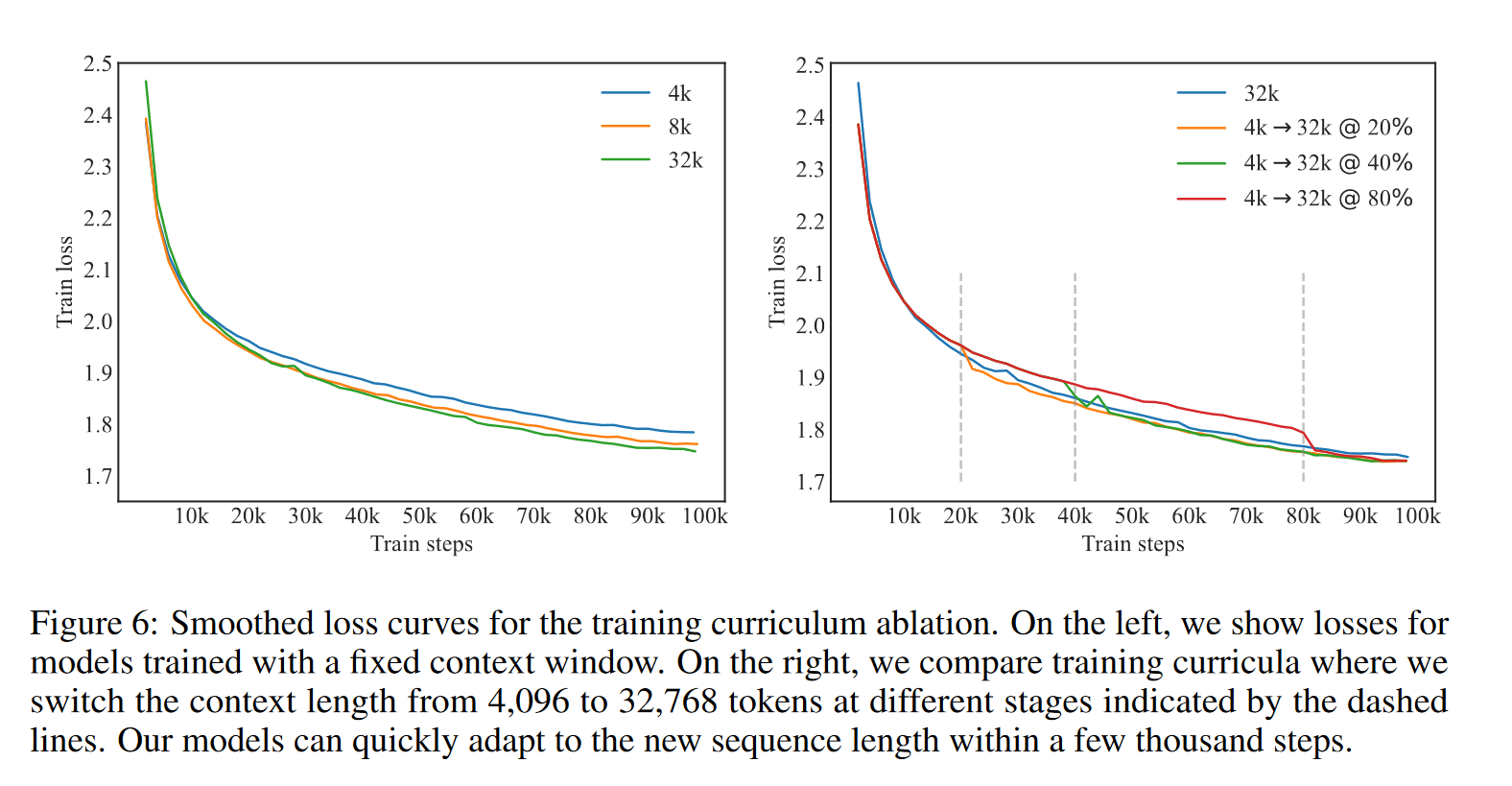
文中尝试了先从 4096 长度开始训练,而后换到 32768 训练。看文中的实验,似乎感觉从 20%-40% 的部分就换到 32k 训练效果会好一点。
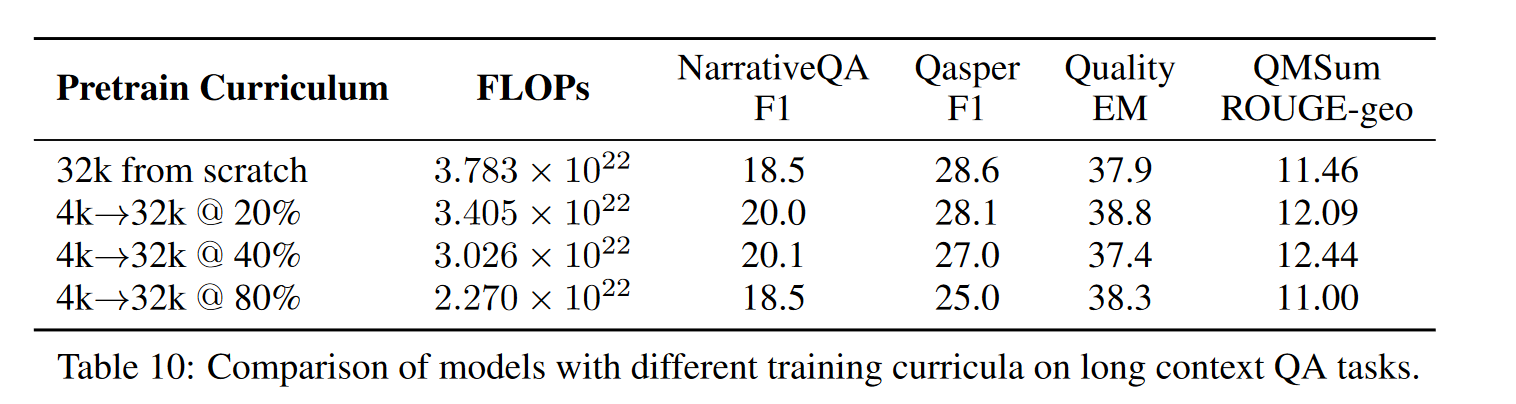
下表中表示,每当长度从 4K 切换到 32k,模型地 loss 都会有进一步地减少。
参考
Perpetual Sampling with LLaMA-30B
LM-INFINITE: SIMPLE ON-THE-FLY LENGTH GENERALIZATION FOR LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS
StreamingLLM: EFFICIENT STREAMING LANGUAGE MODELS WITH ATTENTION SINKS
Transformer 升级之路:7、长度外推性与局部注意力
Transformer 升级之路:8、长度外推性与位置鲁棒性
TRAIN SHORT, TEST LONG: ATTENTION WITH LINEAR BIASES ENABLES INPUT LENGTH EXTRAPOLATION
A Length-Extrapolatable Transformer
Understanding data influence on context scaling: a close look at baseline solution
Effective Long-Context Scaling of Foundation Models
RoPE 外推的缩放法则 —— 尝试外推 RoPE 至 1M 上下文
Extending Context Window of Large Language Models via Positional Interpolation
Understanding data influence on context scaling: a close look at baseline solution