UIE-X 统一图文信息抽取方案
UIE-X
小结:UIE-X 可以看作使用了 Ernie-LayoutX 的框架,同时采用了开源版 UIE (非 T5 版)的 prompt 格式。同时模型权重不同。总体来说,能够在 30-shot 内实现相对好的文档图片信息抽取,uie-x 的推出在一定程度上弥补了 PaddleNLP 中document_intelligence(Ernie-Layout)不能在自定义任务上提高效果的遗憾。参考 UIE-X 文档:UIE-X
UIE-X 文档信息抽取 Pipeline
TaskFlow 中可以查看到 UIE-X 采用了以下 Pipeline。
inputs = self._preprocess(*args)
outputs = self._run_model(inputs)
results = self._postprocess(outputs)
其中 _postprocess 没什么具体作用,只是包装以下输出结果。
输入处理
输入处理步骤在 inputs = self._preprocess(*args) 完成,主要是使用了 OCR,从图片中提取了文字以及对应的 bbox。
# args 为原始输入图片的 path
args = [{"doc": "test.jpg"}] # [Dict{"doc":img_path/pdf_path}]
# inputs = self._preprocess(*args) 输出内容
# 在分析输入文件格式(ocr or pdf)后,_preprocess 使用 paddleOCR 提取了文件基础数据,包括:
doc["image"] = np2base64(image)
doc["offset_x"] = offset_x
doc["offset_y"] = offset_y
doc["img_w"] = img_w
doc["img_h"] = img_h
doc["layout"] = self.ocr(image) # ocr 解析版式以及文字内容
return List[doc]
其中 layout 的结构为 ocr 的结果:
[([275.0, 111.0, 444.0, 161.0], '报告时间:'), ([1333.0, 111.0, 1893.0, 165.0], '报告类型:乙肝五项定量+乙肝前 S1')]
模型预测
主要的预测在 outputs = self._run_model(inputs) 中实现推理使用的模型为 ernie_layoutx 加上一层 linear 层,通过双指针方式进行 span 信息抽取。参考transformers/ernie_layout/modeling/UIEX,UIEX 可以看作使用了 LayoutX 的框架,同时采用了开源版 UIE 的 prompt 格式,模型处初始化权重外,架构主干于 layoutx 相同。而根据 PaddleNLP 介绍内容,UIE-X 的模型权重优势未知。
# outputs = self._run_model(inputs)
def _run_model(self, inputs):
# 主要步骤
raw_inputs = inputs["text"]
_inputs = self._parse_inputs(raw_inputs) # 整理输入格式,提取出 text
results = self._multi_stage_predict(_inputs) # 模型预测
inputs["result"] = results
return inputs
_inputs 为 List,其中元素为:
{"text": text(String), "bbox": bbox(List[List[Int]]), "image": d["image"](base64), "layout": d["layout"]}
改方法的重点在于 self._multi_stage_predict(_inputs),其中主要流程为:
- 对 schema_tree 上的节点,构造以下的 prompt,比如我们的 schema 为:
schema = {'姓名': [
'基本信息',
'兴趣爱好',
'电话号码',
'GPA',
'民族',
'邮箱'
]}
那么采用 bfs 方式构建 prompt:
prompts = ["姓名",f"{姓名}的基本信息",f"{姓名}的电话号码",...] # 其中 f-string 中的姓名会被替换为具体预测结果。
- 对于每个 prompt 我们构建这样的模型输入:
{
"text": string, # 所有 ocr 结果的拼接
"bbox": one_data["bbox"], # 所有 bbox 的结果,根据 ocr 字符顺序拼接
"image": one_data["image"], # 图片数据
"prompt": dbc2sbc(prompt), # 输入的 prompt
}
然后进行模型推理,具体的推理流程于 LayoutX 一样,可以参考 Ernie-Layout 笔记。
数据标注
使用 Label Studio 进行标注。
TaskFlow 快速使用
在 taskflow 中使用示例:
from pprint import pprint
from paddlenlp import Taskflow
schema = {
'姓名': [
'电话',
'邮箱'
]
}
my_ie = Taskflow("information_extraction", model="uie-x-base", schema=schema, task_path='./checkpoint/model', precison='fp16')
与 taskflow 中的 document_intelligence 相比,uie-x-base (information_extraction)支持微调。但模型规模比 document_intelligence 小(uie-x 只有 12 层)。输入方面 document_intelligence 除了 prompt 自由点外,与 UIE-X 均相同。输出方面 document_intelligence 用的 BIO 序列标注,UIE-X 用的 0/1 span 抽取。
因此,对于自定义任务,还是优先使用information_extraction 微调。
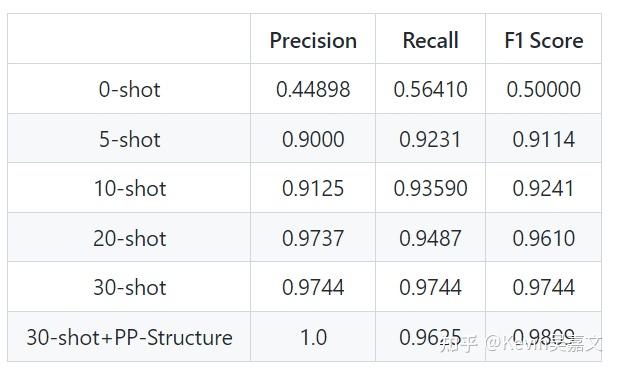
应用效果
从官方给出的微调效果指标看,UIE-X 在自定义任务上的效果还是不错的。但经过笔者测试,自定义任务微调后,模型对于陌生 prompt 内容的预测准确度还不是很理想。
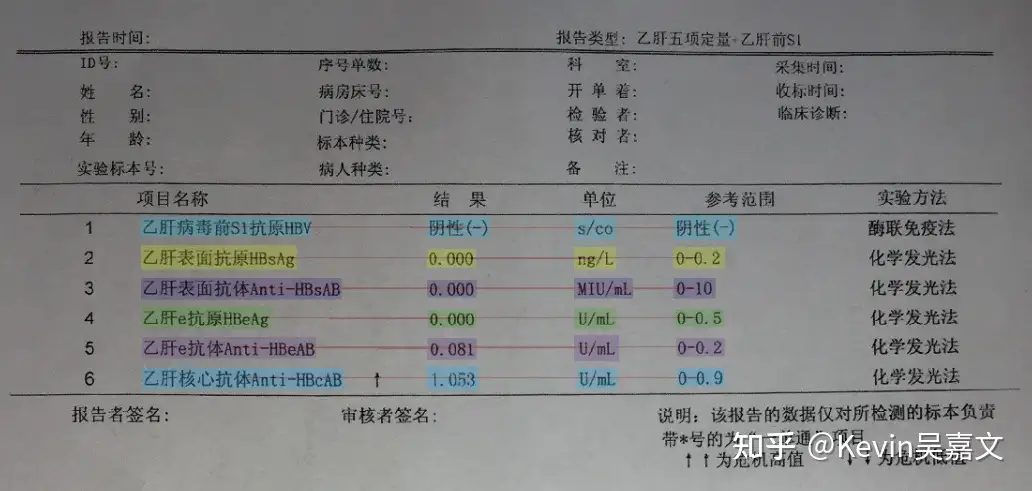
如上图,训练数据中未标记 实验方法,我们在 prompt 中加入预测 实验方法 的需求,预测出来的结果如下:
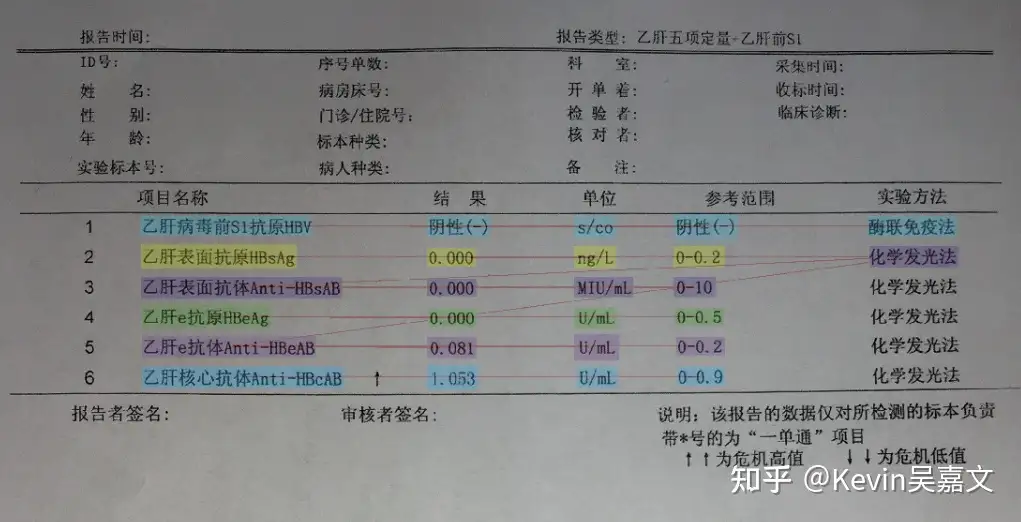
因此建议数据集中,尽可能地覆盖所有 prompt 情况。